

Vous cherchez un déménageur fiable à Laval ? Notre entreprise offre un service complet pour garantir un déménagement sans stress. Nous intervenons rapidement et efficacement dans tous les quartiers de Laval.
Nos déménageurs sont hautement qualifiés pour manipuler tous types d’objets, y compris les plus fragiles. Chaque client bénéficie d’un service adapté à ses besoins spécifiques. Vous pouvez compter sur notre ponctualité, notre rigueur, et notre professionnalisme du début à la fin.
À Laval, nous sommes reconnus pour notre réactivité et notre approche orientée client. livraison Nos camions sont équipés pour tous types de déménagements. Demandez une estimation gratuite aujourd’hui et profitez d’un accompagnement personnalisé pour votre déménagement.
Nous comprenons que chaque déménagement à Laval est unique. Nous offrons des solutions clés en main pour une expérience agréable.
Que ce soit un déménagement résidentiel, commercial ou étudiant, nous avons les ressources nécessaires pour tout gérer. Notre équipe est disponible 7j/7 pour s’adapter à votre emploi du temps. Nous garantissons un service rapide, même pour les déménagements de dernière minute à Laval.
marqueur
Tous vos meubles sont démontés, emballés et réinstallés selon les normes les plus élevées. Profitez de notre expérience pour sécuriser vos effets personnels. numéro À Laval, déménager devient simple avec notre sens du détail reconnu.
Notre philosophie centrée sur le client rend chaque déménagement à Laval fluide et agréable. Nous vous accompagnons du premier contact jusqu'à l’installation finale.


Même les transferts de dernière minute sont possibles grâce à notre équipe réactive. boîte Nous savons gérer la pression et garantir un service rapide et efficace à Laval. Vous êtes entre de bonnes mains.
Nous desservons toutes les zones de Laval avec une connaissance locale inégalée. Peu importe la complexité du lieu, nous adaptons notre matériel. Notre objectif est de faciliter votre déménagement, peu importe les conditions.
Nous offrons des formules flexibles adaptés à tous les budgets. Vous bénéficiez d’un service de qualité, sans frais cachés. Réservez votre créneau dès aujourd’hui pour éviter toute attente de dernière minute.
Vos biens méritent d’être traités avec soin, c’est pourquoi nous utilisons des matériaux d’emballage de qualité. Même les objets fragiles sont protégés avec précision. Votre tranquillité d’esprit est notre priorité.
Notre équipe est disponible et ponctuelle, même pendant les périodes chargées. Chaque mission est prise au sérieux, peu importe sa taille. Nous respectons les délais convenus.
expertise
À Laval, nous avons déjà aidé des centaines de familles grâce à notre approche humaine. Nous offrons une assistance complète, même après le déménagement. Un suivi post-service est assuré pour garantir votre satisfaction.

L’optimisation des trajets nous permet d’agir rapidement, sans perte de temps inutile. Vous gagnez en efficacité.
Nous proposons également des services supplémentaires tels que le nettoyage, le montage de meubles et l’étiquetage. Rien n’est imposé, tout est flexible.
Les clients qui choisissent notre entreprise nous recommandent pour la qualité constante et notre sérieux. Nous bâtissons une relation de confiance à long terme. adhésif Chaque mission est un engagement de qualité.
Déménagement Total à Laval, c’est plus qu’un simple service : c’est une expérience client complète. Nous sommes là avant, pendant, et après votre déménagement. Votre satisfaction est notre moteur.
Vous gagnez du temps et évitez les appels inutiles. Tout se passe en quelques clics.
chariot
Choisissez notre équipe et découvrez un déménagement sans stress, professionnel de bout en bout. Laval mérite une entreprise à la hauteur – et c’est exactement ce que nous offrons.
|
|
This article may be too long to read and navigate comfortably. When this tag was added, its readable prose size was 14,769 words. (June 2024)
|
|
Quebec
Québec (French)
|
|
|---|---|
| Motto(s): | |
| Coordinates: 52°N 72°W / 52°N 72°W[1] | |
| Country | Canada |
| Before confederation | Canada East |
| Confederation | July 1, 1867 (1st, with New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Ontario) |
| Capital | Quebec City |
| Largest city | Montreal |
| Largest metro | Greater Montreal |
| Government
|
|
| • Type | Parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| • Lieutenant Governor | Manon Jeannotte |
| • Premier | François Legault |
| Legislature | National Assembly of Quebec |
| Federal representation | Parliament of Canada |
| House seats | 78 of 338 (23.1%) |
| Senate seats | 24 of 105 (22.9%) |
| Area
|
|
|
• Total
|
1,542,056 km2 (595,391 sq mi) |
| • Land | 1,365,128 km2 (527,079 sq mi) |
| • Water | 176,928 km2 (68,312 sq mi) 11.5% |
| • Rank | 2nd |
| 15.4% of Canada | |
| Population
(2021)
|
|
|
• Total
|
8,501,833[2] |
|
• Estimate
(Q1 2025)
|
9,111,629[3] |
| • Rank | 2nd |
| • Density | 6.23/km2 (16.1/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | in English: Quebecer, Quebecker, Québécois in French: Québécois (m),[4] Québécoise (f)[4] |
| Official languages | French[5] |
| GDP
|
|
| • Rank | 2nd |
| • Total (2022) | C$552.737 billion[6] |
| • Per capita | C$63,651 (9th) |
| HDI
|
|
| • HDI (2019) | 0.916[7]—Very high (9th) |
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern Time Zone for most of the province[8]) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 |
| Canadian postal abbr. |
QC[9]
|
| Rankings include all provinces and territories | |
Quebec[a] is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the largest province by area[b] and located in Central Canada. The province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast and a coastal border with the territory of Nunavut. In the south, it shares a border with the United States[c].
Between 1534 and 1763, what is now Quebec was the French colony of Canada and was the most developed colony in New France. Following the Seven Years' War, Canada became a British colony, first as the Province of Quebec (1763–1791), then Lower Canada (1791–1841), and lastly part of the Province of Canada (1841–1867) as a result of the Lower Canada Rebellion. It was confederated with Ontario, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick in 1867. Until the early 1960s, the Catholic Church played a large role in the social and cultural institutions in Quebec. However, the Quiet Revolution of the 1960s to 1980s increased the role of the Government of Quebec in l'État québécois (the public authority of Quebec).
The Government of Quebec functions within the context of a Westminster system and is both a liberal democracy and a constitutional monarchy. The Premier of Quebec acts as head of government. Independence debates have played a large role in Quebec politics. Quebec society's cohesion and specificity is based on three of its unique statutory documents: the Quebec Charter of Human Rights and Freedoms, the Charter of the French Language, and the Civil Code of Quebec. Furthermore, unlike elsewhere in Canada, law in Quebec is mixed: private law is exercised under a civil-law system, while public law is exercised under a common-law system.
Quebec's official language is French; Québécois French is the regional variety. Quebec is the only Francophone-majority province. The economy of Quebec is mainly supported by its large service sector and varied industrial sector. For exports, it leans on the key industries of aeronautics, hydroelectricity, mining, pharmaceuticals, aluminum, wood, and paper. Quebec is well known for producing maple syrup, for its comedy, and for making hockey one of the most popular sports in Canada. It is also renowned for its culture; the province produces literature, music, films, TV shows, festivals, and more.
The name Québec comes from an Algonquin word meaning 'narrow passage' or 'strait'.[13] The name originally referred to the area around Quebec City where the Saint Lawrence River narrows to a cliff-lined gap. Early variations in the spelling included Québecq and Kébec.[14] French explorer Samuel de Champlain chose the name Québec in 1608 for the colonial outpost he would use as the administrative seat for New France.[15]

The Paleo-Indians, theorized to have migrated from Asia to America between 20,000 and 14,000 years ago, were the first people to establish themselves on the lands of Quebec, arriving after the Laurentide Ice Sheet melted roughly 11,000 years ago.[16][17] From them, many ethnocultural groups emerged. By the European explorations of the 1500s, there were eleven Indigenous peoples: the Inuit and ten First Nations – the Abenakis, Algonquins (or Anichinabés), Atikamekw, Cree, Huron-Wyandot, Maliseet, Miꞌkmaqs, Iroquois, Innu and Naskapis.[18] Algonquians organized into seven political entities and lived nomadic lives based on hunting, gathering, and fishing.[19] Inuit fished and hunted whales and seals along the coasts of Hudson and Ungava Bays.[20]
In the 15th century, the Byzantine Empire fell, prompting Western Europeans to search for new sea routes to the Far East.[21] Around 1522–23, Giovanni da Verrazzano persuaded King Francis I of France to commission an expedition to find a western route to Cathay (China) via a Northwest Passage. Though this expedition was unsuccessful, it established the name New France for northeast North America.[22] In his first expedition ordered from the Kingdom of France, Jacques Cartier became the first European explorer to discover and map Quebec when he landed in Gaspé on July 24, 1534.[23] In the second expedition, in 1535, Cartier explored the lands of Stadacona and named the village and its surrounding territories Canada (from kanata, 'village' in Iroquois). Cartier returned to France with about 10 St. Lawrence Iroquoians, including Chief Donnacona. In 1540, Donnacona told the legend of the Kingdom of Saguenay to the King, inspiring him to order a third expedition, this time led by Jean-François de La Rocque de Roberval; it was unsuccessful in its goal of finding the kingdom.[24]
After these expeditions, France mostly abandoned North America for 50 years because of its financial crisis; France was involved in the Italian Wars and religious wars.[25] Around 1580, the rise of the fur trade reignited French interest; New France became a colonial trading post.[26] In 1603, Samuel de Champlain travelled to the Saint Lawrence River and, on Pointe Saint-Mathieu, established a defence pact with the Innu, Maliseet and Micmacs, that would be "a decisive factor in the maintenance of a French colonial enterprise in America despite an enormous numerical disadvantage vis-à-vis the British".[27] Thus also began French military support to the Algonquian and Huron peoples against Iroquois attacks; these became known as the Iroquois Wars and lasted from the early 1600s to the early 1700s.[28]

In 1608, Samuel de Champlain[29] returned to the region as head of an exploration party. On July 3, 1608, with the support of King Henry IV, he founded the Habitation de Québec (now Quebec City) and made it the capital of New France and its regions.[26] The settlement was built as a permanent fur trading outpost, where First Nations traded furs for French goods, such as metal objects, guns, alcohol, and clothing.[30] Missionary groups arrived in New France after the founding of Quebec City. Coureurs des bois and Catholic missionaries used river canoes to explore the interior and establish fur trading forts.[31][32]
The Compagnie des Cent-Associés, which had been granted a royal mandate to manage New France in 1627, introduced the Custom of Paris and the seigneurial system, and forbade settlement by anyone other than Catholics.[33] In 1629, Quebec City surrendered, without battle, to English privateers during the Anglo-French War; in 1632, the English king agreed to return it with the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye. Trois-Rivières was founded at de Champlain's request in 1634.[34] Paul de Chomedey de Maisonneuve founded Ville-Marie (now Montreal) in 1642.
In 1663, the Company of New France ceded Canada to King Louis XIV, who made New France into a royal province of France.[35] New France was now a true colony administered by the Sovereign Council of New France from Quebec City. A governor-general, governed Canada and its administrative dependencies: Acadia, Louisiana and Plaisance.[36] The French settlers were mostly farmers and known as "Canadiens" or "Habitants". Though there was little immigration,[37] the colony grew because of the Habitants' high birth rates.[38][39] In 1665, the Carignan-Salières regiment developed the string of fortifications known as the "Valley of Forts" to protect against Iroquois invasions and brought with them 1,200 new men.[40] To redress the gender imbalance and boost population growth, King Louis XIV sponsored the passage of approximately 800 young French women (King's Daughters) to the colony.[35] In 1666, intendant Jean Talon organized the first census and counted 3,215 Habitants. Talon enacted policies to diversify agriculture and encourage births, which, in 1672, had increased the population to 6,700.[41]
New France's territory grew to extend from Hudson Bay to the Gulf of Mexico, and would encompass the Great Lakes.[42] In the early 1700s, Governor Callières concluded the Great Peace of Montreal, which not only confirmed the alliance between the Algonquian and New France, but definitively ended the Iroquois Wars.[43] From 1688 onwards, the fierce competition between the French and British to control North America's interior and monopolize fur trade pitted New France and its Indigenous allies against the Iroquois and English in four successive wars called the French and Indian Wars by Americans, and the Intercolonial Wars in Quebec.[44] The first three were King William's War (1688–1697), Queen Anne's War (1702–1713), and King George's War (1744–1748). In 1713, following the Peace of Utrecht, the Duke of Orléans ceded Acadia and Plaisance Bay to Great Britain, but retained Île Saint-Jean, and Île-Royale where the Fortress of Louisbourg was subsequently erected. These losses were significant since Plaisance Bay was the primary communication route between New France and France, and Acadia contained 5,000 Acadians.[45][46] In the siege of Louisbourg (1745), the British were victorious, but returned the city to France after war concessions.[47]

The last of the four French and Indian Wars was the Seven Years' War ("The War of the Conquest" in Quebec) and lasted from 1754 to 1763.[48][49] In 1754, tensions escalated for control of the Ohio Valley, as authorities in New France became more aggressive in efforts to expel British traders and colonists.[50] In 1754, George Washington launched a surprise attack on a group of sleeping Canadien soldiers, known as the Battle of Jumonville Glen, the first battle of the war. In 1755, Governor Charles Lawrence and Officer Robert Monckton ordered the forceful expulsion of the Acadians. In 1758, on Île-Royale, British General James Wolfe besieged and captured the Fortress of Louisbourg.[51] This allowed him to control access to the Gulf of St. Lawrence through the Cabot Strait. In 1759, he besieged Quebec for three months from Île d'Orléans.[52] Then, Wolfe stormed Quebec and fought against Montcalm for control of the city in the Battle of the Plains of Abraham. After a British victory, the king's lieutenant and Lord of Ramezay concluded the Articles of Capitulation of Quebec. During the spring of 1760, the Chevalier de Lévis besieged Quebec City and forced the British to entrench themselves during the Battle of Sainte-Foy. However, loss of French vessels sent to resupply New France after the fall of Quebec City during the Battle of Restigouche marked the end of France's efforts to retake the colony. Governor Pierre de Rigaud, marquis de Vaudreuil-Cavagnial signed the Articles of Capitulation of Montreal on September 8, 1760.
While awaiting the results of the Seven Years' War in Europe, New France was put under a British military regime led by Governor James Murray.[53] In 1762, Commander Jeffery Amherst ended the French presence in Newfoundland at the Battle of Signal Hill. France secretly ceded the western part of Louisiana and the Mississippi River Delta to Spain via the Treaty of Fontainebleau. On February 10, 1763, the Treaty of Paris concluded the war. France ceded its North American possessions to Great Britain.[54] Thus, France had put an end to New France and abandoned the remaining 60,000 Canadiens, who sided with the Catholic clergy in refusing to take an oath to the British Crown.[55] The rupture from France would provoke a transformation within the descendants of the Canadiens that would eventually result in the birth of a new nation.[56]

After the British acquired Canada in 1763, the British government established a constitution for the newly acquired territory, under the Royal Proclamation.[57] The Canadiens were subordinated to the government of the British Empire and circumscribed to a region of the St. Lawrence Valley and Anticosti Island called the Province of Quebec. With unrest growing in their southern colonies, the British were worried that the Canadiens might support what would become the American Revolution. To secure allegiance to the British crown, Governor James Murray and later Governor Guy Carleton promoted the need for accommodations, resulting in the enactment of the Quebec Act[58] of 1774. This act allowed Canadiens to regain their civil customs, return to the seigneural system, regain certain rights including use of French, and reappropriate their old territories: Labrador, the Great Lakes, the Ohio Valley, Illinois Country and the Indian Territory.[59]
As early as 1774, the Continental Congress of the separatist Thirteen Colonies attempted to rally the Canadiens to its cause. However, its military troops failed to defeat the British counteroffensive during its Invasion of Quebec in 1775. Most Canadiens remained neutral, though some regiments allied themselves with the Americans in the Saratoga campaign of 1777. When the British recognized the independence of the rebel colonies at the signing of the Treaty of Paris of 1783, it conceded Illinois and the Ohio Valley to the newly formed United States and denoted the 45th parallel as its border, drastically reducing Quebec's size.
Some United Empire Loyalists from the US migrated to Quebec and populated various regions.[60] Dissatisfied with the legal rights under the French seigneurial régime which applied in Quebec, and wanting to use the British legal system to which they were accustomed, the Loyalists protested to British authorities until the Constitutional Act of 1791 was enacted, dividing the Province of Quebec into two distinct colonies starting from the Ottawa River: Upper Canada to the west (predominantly Anglo-Protestant) and Lower Canada to the east (Franco-Catholic). Lower Canada's lands consisted of the coasts of the Saint Lawrence River, Labrador and Anticosti Island, with the territory extending north to Rupert's Land, and south, east and west to the borders with the US, New Brunswick, and Upper Canada. The creation of Upper and Lower Canada allowed Loyalists to live under British laws and institutions, while Canadiens could maintain their French civil law and Catholic religion. Governor Haldimand drew Loyalists away from Quebec City and Montreal by offering free land on the north shore of Lake Ontario to anyone willing to swear allegiance to George III. During the War of 1812, Charles-Michel de Salaberry became a hero by leading the Canadian troops to victory at the Battle of the Chateauguay. This loss caused the Americans to abandon the Saint Lawrence Campaign, their major strategic effort to conquer Canada.

Gradually, the Legislative Assembly of Lower Canada, who represented the people, came into conflict with the superior authority of the Crown and its appointed representatives. Starting in 1791, the government of Lower Canada was criticized and contested by the Parti canadien. In 1834, the Parti canadien presented its 92 resolutions, political demands which expressed loss of confidence in the British monarchy. Discontentment intensified throughout the public meetings of 1837, and the Lower Canada Rebellion began in 1837.[62] In 1837, Louis-Joseph Papineau and Robert Nelson led residents of Lower Canada to form an armed group called the Patriotes. They made a Declaration of Independence in 1838, guaranteeing rights and equality for all citizens without discrimination.[63] Their actions resulted in rebellions in both Lower and Upper Canada. The Patriotes were victorious in their first battle, the Battle of Saint-Denis. However, they were unorganized and badly equipped, leading to their loss against the British army in the Battle of Saint-Charles, and defeat in the Battle of Saint-Eustache.[61]
In response to the rebellions, Lord Durham was asked to undertake a study and prepare a report offering a solution to the British Parliament.[64] Durham recommended that Canadiens be culturally assimilated, with English as their only official language. To do this, the British passed the Act of Union 1840, which merged Upper Canada and Lower Canada into a single colony: the Province of Canada. Lower Canada became the francophone and densely populated Canada East, and Upper Canada became the anglophone and sparsely populated Canada West. This union, unsurprisingly, was the main source of political instability until 1867. Despite their population gap, Canada East and Canada West obtained an identical number of seats in the Legislative Assembly of the Province of Canada, which created representation problems. In the beginning, Canada East was underrepresented because of its superior population size. Over time, however, massive immigration from the British Isles to Canada West occurred. Since the two regions continued to have equal representation, this meant it was now Canada West that was under-represented. The representation issues were called into question by debates on "Representation by Population". The British population began to use the term "Canadian", referring to Canada, their place of residence. The French population, who had thus far identified as "Canadiens", began to be identified with their ethnic community under the name "French Canadian" as they were a "French of Canada".[65]
As access to new lands remained problematic because they were still monopolized by the Clique du Château, an exodus of Canadiens towards New England began and went on for the next hundred years. This phenomenon is known as the Grande Hémorragie and threatened the survival of the Canadien nation. The massive British immigration ordered from London that followed the failed rebellion, compounded this. To combat it, the Church adopted the revenge of the cradle policy. In 1844, the capital of the Province of Canada was moved from Kingston to Montreal.[66] During Ireland's Great Potato Famine (1845-1852), nearly 100,000 Irish refugees passed through Grosse-Île's quarantine station, with many settling in Quebec and integrating into French-Canadian society.[67][68]
Political unrest came to a head in 1849, when English Canadian rioters set fire to the Parliament Building in Montreal following the enactment of the Rebellion Losses Bill, a law that compensated French Canadians whose properties were destroyed during the rebellions of 1837–1838.[69] This bill, resulting from the Baldwin-La Fontaine coalition and Lord Elgin's advice, was important as it established the notion of responsible government.[70] In 1854, the seigneurial system was abolished, the Grand Trunk Railway was built and the Canadian–American Reciprocity Treaty was implemented. In 1866, the Civil Code of Lower Canada was adopted.[71][72][73]

In 1864, negotiations began for Canadian Confederation between the Province of Canada, New Brunswick and Nova Scotia at the Charlottetown Conference and Quebec Conference.
After having fought as a Patriote, George-Étienne Cartier entered politics in the Province of Canada, becoming one of the co-premiers and advocate for the union of the British North American provinces. He became a leading figure at the Quebec Conference, which produced the Quebec Resolutions, the foundation for Canadian Confederation.[74] Recognized as a Father of Confederation, he successfully argued for the establishment of the province of Quebec, initially composed of the historic heart of the territory of the French Canadian nation and where French Canadians would most likely retain majority status.
Following the London Conference of 1866, the Quebec Resolutions were implemented as the British North America Act, 1867 and brought into force on July 1, 1867, creating Canada. Canada was composed of four founding provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Ontario and Quebec. These last two came from splitting the Province of Canada, and used the old borders of Lower Canada for Quebec, and Upper Canada for Ontario. On July 15, 1867, Pierre-Joseph-Olivier Chauveau became Quebec's first premier.
From Confederation until World War I, the Catholic Church was at its peak. The objective of clerico-nationalists was promoting the values of traditional society: family, French, the Catholic Church and rural life. Events such as the North-West Rebellion, the Manitoba Schools Question and Ontario's Regulation 17 turned the promotion and defence of the rights of French Canadians into an important concern.[75] Under the aegis of the Catholic Church and the political action of Henri Bourassa, symbols of national pride were developed, like the Flag of Carillon, and "O Canada" – a patriotic song composed for Saint-Jean-Baptiste Day. Many organizations went on to consecrate the affirmation of the French-Canadian people, including the caisses populaires Desjardins in 1900, the Club de hockey Canadien in 1909, Le Devoir in 1910, the Congress on the French language in Canada in 1912, and L'Action nationale in 1917. In 1885, liberal and conservative MPs formed the Parti national out of anger with the previous government for not having interceded in the execution of Louis Riel.[76]
In 1898, the Canadian Parliament enacted the Quebec Boundary Extension Act, 1898, which gave Quebec part of Rupert's Land, which Canada had bought from the Hudson's Bay Company in 1870.[77] This act expanded the boundaries of Quebec northward. In 1909, the government passed a law obligating wood and pulp to be transformed in Quebec, which helped slow the Grande Hémorragie by allowing Quebec to export its finished products to the US instead of its labour force.[78] In 1910, Armand Lavergne passed the Lavergne Law, the first language legislation in Quebec. It required use of French alongside English on tickets, documents, bills and contracts issued by transportation and public utility companies. At this time, companies rarely recognized the majority language of Quebec.[79] Clerico-nationalists eventually started to fall out of favour in the federal elections of 1911. In 1912, the Canadian Parliament enacted the Quebec Boundaries Extension Act, 1912, which gave Quebec another part of Rupert's Land: the District of Ungava.[80] This extended the borders of Quebec northward to the Hudson Strait.
When World War I broke out, Canada was automatically involved and many English Canadians volunteered. However, because they did not feel the same connection to the British Empire and there was no direct threat to Canada, French Canadians saw no reason to fight. By late 1916, casualties were beginning to cause reinforcement problems. After enormous difficulty in the federal government, because almost every French-speaking MP opposed conscription while almost all English-speaking MPs supported it, the Military Service Act became law on August 29, 1917.[81] French Canadians protested in what is now called the Conscription Crisis of 1917, which led to the Quebec riot.[82]
In 1919, the prohibition of spirits was enacted following a provincial referendum.[83] But, prohibition was abolished in 1921 due to the Alcoholic Beverages Act which created the Commission des liqueurs du Québec.[84] In 1927, the British Judicial Committee of the Privy Council drew a clear border between northeast Quebec and south Labrador. However, the Quebec government did not recognize the ruling of the Judicial Committee, resulting in a boundary dispute which remains ongoing. The Statute of Westminster 1931 was enacted, and confirmed the autonomy of the Dominions – including Canada and its provinces – from the UK, as well as their free association in the Commonwealth.[85] In the 1930s, Quebec's economy was affected by the Great Depression because it greatly reduced US demand for Quebec exports. Between 1929-32 the unemployment rate increased from 8% to 26%. In an attempt to remedy this, the Quebec government enacted infrastructure projects, campaigns to colonize distant regions, financial assistance to farmers, and the secours directs – the ancestor to Canada's Employment Insurance.[86]

French Canadians remained opposed to conscription during the Second World War. When Canada declared war in September 1939, the federal government pledged not to conscript soldiers for overseas service. As the war went on, more and more English Canadians voiced support for conscription, despite firm opposition from French Canada. Following a 1942 poll that showed 73% of Quebec's residents were against conscription, while 80% or more were for conscription in every other province, the federal government passed Bill 80 for overseas service. Protests exploded and the Bloc Populaire emerged to fight conscription.[81] The stark differences between the values of French and English Canada popularized the expression the "Two Solitudes".
In the wake of the conscription crisis, Maurice Duplessis of the Union Nationale ascended to power and implemented conservative policies known as the Grande Noirceur. He focused on defending provincial autonomy, Quebec's Catholic and francophone heritage, and laissez-faire liberalism instead of the emerging welfare state.[87] However, as early as 1948, French Canadian society began to develop new ideologies and desires in response to societal changes such as the television, the baby boom, workers' conflicts, electrification of the countryside, emergence of a middle class, the rural exodus and urbanization, expansion of universities and bureaucracies, creation of motorways, renaissance of literature and poetry, and others.

The Quiet Revolution was a period of modernization, secularization and social reform, where French Canadians expressed their concern and dissatisfaction with their inferior socioeconomic position, and the cultural assimilation of francophone minorities in the English-majority provinces. It resulted in the formation of the modern Québécois identity and Quebec nationalism.[88][89] In 1960, the Liberal Party of Quebec was brought to power with a two-seat majority, having campaigned with the slogan "It's time for things to change". This government made reforms in social policy, education, health and economic development. It created the Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec, Labour Code, Ministry of Social Affairs, Ministry of Education, Office québécois de la langue française, Régie des rentes and Société générale de financement. In 1962, the government of Quebec dismantled the financial syndicates of Saint Jacques Street. Quebec began to nationalize its electricity. In order to buy out all the private electric companies and build new Hydro-Québec dams, Quebec was lent $300 million by the US in 1962,[90] and $100 million by British Columbia in 1964.[91]
The Quiet Revolution was particularly characterized by the 1962 Liberal Party's slogan "Masters in our own house", which, to the Anglo-American conglomerates that dominated the economy and natural resources, announced a collective will for freedom of the French-Canadian people.[92] As a result of confrontations between the lower clergy and the laity, state institutions began to deliver services without the assistance of the church, and many parts of civil society began to be more secular. In 1965, the Royal Commission on Bilingualism and Biculturalism[93] wrote a preliminary report underlining Quebec's distinct character, and promoted open federalism, a political attitude guaranteeing Quebec a minimum amount of consideration.[94][95] To favour Quebec during its Quiet Revolution, Lester B. Pearson adopted a policy of open federalism.[96][97] In 1966, the Union Nationale was re-elected and continued on with major reforms.[98]

In 1967, President of France Charles de Gaulle visited Quebec, to attend Expo 67. There, he addressed a crowd of more than 100,000, making a speech ending with the exclamation: "Long live free Quebec". This declaration had a profound effect on Quebec by bolstering the burgeoning modern Quebec sovereignty movement and resulting in a political crisis between France and Canada. Following this, various civilian groups developed, sometimes confronting public authority, for example in the October Crisis of 1970.[99] The meetings of the Estates General of French Canada in 1967 marked a tipping point where relations between francophones of America, and especially francophones of Canada, ruptured. This breakdown affected Quebec society's evolution.[100]
In 1968, class conflicts and changes in mentalities intensified.[101] Option Quebec sparked a constitutional debate on the political future of the province by pitting federalist and sovereignist doctrines against each other. In 1969, the federal Official Languages Act was passed to introduce a linguistic context conducive to Quebec's development.[102][103] In 1973, the liberal government of Robert Bourassa initiated the James Bay Project on La Grande River. In 1974, it enacted the Official Language Act, which made French the official language of Quebec. In 1975, it established the Charter of Human Rights and Freedoms and the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement.

Quebec's first modern sovereignist government, led by René Lévesque, materialized when the Parti Québécois was brought to power in the 1976 Quebec general election.[104] The Charter of the French Language came into force the following year, which increased the use of French. Between 1966-69, the Estates General of French Canada confirmed the state of Quebec to be the nation's fundamental political milieu and for it to have the right to self-determination.[105][106] In the 1980 referendum on sovereignty, 60% were against.[107] After the referendum, Lévesque went back to Ottawa to start negotiating constitutional changes. On November 4, 1981, the Kitchen Accord took place. Delegations from the other nine provinces and the federal government reached an agreement in the absence of Quebec's delegation, which had left for the night.[108] Because of this, the National Assembly refused to recognize the new Constitution Act, 1982, which patriated the Canadian constitution and made modifications to it.[109] The 1982 amendments apply to Quebec despite Quebec never having consented to it.[110]
Between 1982-92, the Quebec government's attitude changed to prioritize reforming the federation. Attempts at constitutional amendments by the Mulroney and Bourassa governments ended in failure with the Meech Lake Accord of 1987 and the Charlottetown Accord of 1992, resulting in the creation of the Bloc Québécois.[111][112] In 1995, Jacques Parizeau called a referendum on Quebec's independence from Canada. This consultation ended in failure for sovereignists, though the outcome was very close: 50.6% "no" and 49.4% "yes".[113][114][115]
In 1998, following the Supreme Court of Canada's decision on the Reference Re Secession of Quebec, the Parliaments of Canada and Quebec defined the legal frameworks within which their respective governments would act in another referendum. On October 30, 2003, the National Assembly voted unanimously to affirm "that the people of Québec form a nation".[116] On November 27, 2006, the House of Commons passed a symbolic motion declaring "that this House recognize that the Québécois form a nation within a united Canada."[117] In 2007, the Parti Québécois was pushed back to official opposition in the National Assembly, with the Liberal party leading. During the 2011 Canadian federal elections, Quebec voters rejected the Bloc Québécois in favour of the previously minor New Democratic Party (NDP). As the NDP's logo is orange, this was called the "orange wave".[118] After three subsequent Liberal governments, the Parti Québécois regained power in 2012 and its leader, Pauline Marois, became the first female premier of Quebec.[119] The Liberal Party of Quebec then returned to power in 2014.[120] In 2018, the Coalition Avenir Québec won the provincial general elections.[121] Between 2020-21, Quebec took measures against the COVID-19 pandemic.[122] In 2022, Coalition Avenir Québec, led by Quebec's premier François Legault, increased its parliamentary majority in the provincial general elections.[123]

Located in the eastern part of Canada, Quebec occupies a territory nearly three times the size of France.[124] It holds an area of 1.5 million square kilometres (0.58 million square miles) and its borders are more than 12,000 km (7,500 mi) long.[125][126] Most of Quebec is very sparsely populated.[citation needed] The most populous physiographic region is the Great Lakes–St. Lawrence Lowlands. The combination of rich soils and the lowlands' relatively warm climate makes this valley the most prolific agricultural area of Quebec. The rural part of the landscape is divided into narrow rectangular tracts of land that extend from the river and date back to the seigneurial system.
Quebec's topography is very different from one region to another due to the varying composition of the ground, the climate, and the proximity to water. More than 95% of Quebec's territory, including the Labrador Peninsula, lies within the Canadian Shield.[127] It is generally a quite flat and exposed mountainous terrain interspersed with higher points such as the Laurentian Mountains in southern Quebec, the Otish Mountains in central Quebec and the Torngat Mountains near Ungava Bay. While low and medium altitude peaks extend from western Quebec to the far north, high altitudes mountains emerge in the Capitale-Nationale region to the extreme east. Quebec's highest point at 1,652 metres (5,420 ft) is Mont d'Iberville, known in English as Mount Caubvick.[128] In the Labrador Peninsula portion of the Shield, the far northern region of Nunavik includes the Ungava Peninsula and consists of flat Arctic tundra inhabited mostly by the Inuit. Further south is the Eastern Canadian Shield taiga ecoregion and the Central Canadian Shield forests. The Appalachian region has a narrow strip of ancient mountains along the southeastern border of Quebec.[129]

Quebec has one of the world's largest reserves of fresh water,[130] occupying 12% of its surface[131] and representing 3% of the world's renewable fresh water.[132] More than half a million lakes and 4,500 rivers[130] empty into the Atlantic Ocean, through the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the Arctic Ocean, by James, Hudson, and Ungava bays. The largest inland body of water is the Caniapiscau Reservoir; Lake Mistassini is the largest natural lake.[133] The Saint Lawrence River has some of the world's largest sustaining inland Atlantic ports. Since 1959, the Saint Lawrence Seaway has provided a navigable link between the Atlantic Ocean and the Great Lakes.
The public lands of Quebec cover approximately 92% of its territory, including almost all of the bodies of water. Protected areas can be classified into about twenty different legal designations (ex. exceptional forest ecosystem, protected marine environment, national park, biodiversity reserve, wildlife reserve, zone d'exploitation contrôlée (ZEC), etc.).[134] More than 2,500 sites in Quebec today are protected areas.[135] As of 2013, protected areas comprise 9.14% of Quebec's territory.[136]
The ecological classification of Quebec territory established by the Ministry of Forests, Wildlife and Parks 2021, is presented in 9 levels, it includes the diversity of terrestrial ecosystems throughout Quebec while taking into account both the characteristics of the vegetation (physiognomy, structure and composition) and the physical environment (relief, geology, geomorphology, hydrography).[129]
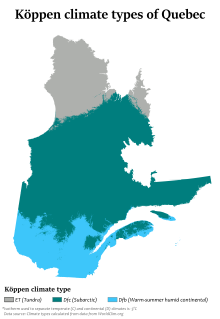
In general, the climate of Quebec is cold and humid, with variations determined by latitude, maritime and elevation influences.[137] Because of the influence of both storm systems from the core of North America and the Atlantic Ocean, precipitation is abundant throughout the year, with most areas receiving more than 1,000 mm (39 in) of precipitation, including over 300 cm (120 in) of snow in many areas.[138] During the summer, severe weather patterns (such as tornadoes and severe thunderstorms) occur occasionally.[139]

Quebec is divided into four climatic zones: arctic, subarctic, humid continental and East maritime. From south to north, average temperatures range in summer between 25 and 5 °C (77 and 41 °F) and, in winter, between −10 and −25 °C (14 and −13 °F).[140][141] In periods of intense heat and cold, temperatures can reach 35 °C (95 °F) in the summer[142] and −40 °C (−40 °F) during the Quebec winter,[142] Most of central Quebec, ranging from 51 to 58 degrees North has a subarctic climate (Köppen Dfc).[137] Winters are long, very cold, and snowy, and among the coldest in eastern Canada, while summers are warm but very short due to the higher latitude and the greater influence of Arctic air masses. Precipitation is also somewhat less than farther south, except at some of the higher elevations. The northern regions of Quebec have an arctic climate (Köppen ET), with very cold winters and short, much cooler summers.[137] The primary influences in this region are the Arctic Ocean currents (such as the Labrador Current) and continental air masses from the High Arctic.
The all-time record high temperature was 40.0 °C (104.0 °F) and the all-time record low was −51.0 °C (−59.8 °F).[143] The all-time record of the greatest precipitation in winter was established in winter 2007–2008, with more than five metres[144] of snow in the area of Quebec City.[145] March 1971, however, saw the "Century's Snowstorm" with more than 40 cm (16 in) in Montreal to 80 cm (31 in) in Mont Apica of snow within 24 hours in many regions of southern Quebec. The winter of 2010 was the warmest and driest recorded in more than 60 years.[146]

Given the geology of the province and its different climates, there are a number of large areas of vegetation in Quebec. These areas, listed in order from the northernmost to the southernmost are: the tundra, the taiga, the Canadian boreal forest (coniferous), mixed forest and deciduous forest.[127] On the edge of Ungava Bay and Hudson Strait is the tundra, whose flora is limited to lichen with less than 50 growing days per year. Further south, the climate is conducive to the growth of the Canadian boreal forest, bounded on the north by the taiga. Not as arid as the tundra, the taiga is associated with the subarctic regions of the Canadian Shield[147] and is characterized by a greater number of both plant (600) and animal (206) species. The taiga covers about 20% of the total area of Quebec.[127] The Canadian boreal forest is the northernmost and most abundant of the three forest areas in Quebec that straddle the Canadian Shield and the upper lowlands of the province. Given a warmer climate, the diversity of organisms is also higher: there are about 850 plant species and 280 vertebrate species. The mixed forest is a transition zone between the Canadian boreal forest and deciduous forest. This area contains a diversity of plant (1000) and vertebrates (350) species, despite relatively cool temperatures. The ecozone mixed forest is characteristic of the Laurentians, the Appalachians and the eastern lowland forests.[147] The third most northern forest area is characterized by deciduous forests. Because of its climate, this area has the greatest diversity of species, including more than 1600 vascular plants and 440 vertebrates.
The total forest area of Quebec is estimated at 750,300 km2 (289,700 sq mi).[148] From the Abitibi-Témiscamingue to the North Shore, the forest is composed primarily of conifers such as the Abies balsamea, the jack pine, the white spruce, the black spruce and the tamarack. The deciduous forest of the Great Lakes–St. Lawrence Lowlands is mostly composed of deciduous species such as the sugar maple, the red maple, the white ash, the American beech, the butternut (white walnut), the American elm, the basswood, the bitternut hickory and the northern red oak as well as some conifers such as the eastern white pine and the northern whitecedar. The distribution areas of the paper birch, the trembling aspen and the mountain ash cover more than half of Quebec's territory.[149]
Biodiversity of the estuary and gulf of Saint Lawrence River[150] includes aquatic mammal wildlife, such as the blue whale, the beluga, the minke whale and the harp seal (earless seal). The Nordic marine animals include the walrus and the narwhal.[151] Inland waters are populated by small to large freshwater fish, such as the largemouth bass, the American pickerel, the walleye, the Acipenser oxyrinchus, the muskellunge, the Atlantic cod, the Arctic char, the brook trout, the Microgadus tomcod (tomcod), the Atlantic salmon, and the rainbow trout.[152]
Among the birds commonly seen in the southern part of Quebec are the American robin, the house sparrow, the red-winged blackbird, the mallard, the common grackle, the blue jay, the American crow, the black-capped chickadee, some warblers and swallows, the starling and the rock pigeon.[153] Avian fauna includes birds of prey like the golden eagle, the peregrine falcon, the snowy owl and the bald eagle. Sea and semi-aquatic birds seen in Quebec are mostly the Canada goose, the double-crested cormorant, the northern gannet, the European herring gull, the great blue heron, the sandhill crane, the Atlantic puffin and the common loon.[154]
The large land wildlife includes the white-tailed deer, the moose, the muskox, the caribou (reindeer), the American black bear and the polar bear. The medium-sized land wildlife includes the cougar, the coyote, the eastern wolf, the bobcat, the Arctic fox, the fox, etc. The small animals seen most commonly include the eastern grey squirrel, the snowshoe hare, the groundhog, the skunk, the raccoon, the chipmunk and the Canadian beaver.

Quebec is founded on the Westminster system, and is both a liberal democracy and a constitutional monarchy with parliamentary regime. The head of government in Quebec is the premier (called premier ministre in French), who leads the largest party in the unicameral National Assembly (Assemblée Nationale) from which the Executive Council of Quebec is appointed. The Conseil du trésor supports the ministers of the Executive Council in their function of stewardship of the state. The lieutenant governor represents the King of Canada.[155][156]
Quebec has 78 members of Parliament (MPs) in the House of Commons of Canada.[157] They are elected in federal elections. At the level of the Senate of Canada, Quebec is represented by 24 senators, which are appointed on the advice of the prime minister of Canada.[158]
The Quebec government holds administrative and police authority in its areas of exclusive jurisdiction. The Parliament of the 43rd legislature is made up of the following parties: Coalition Avenir Québec (CAQ), Parti libéral du Québec (PLQ), Québec solidaire (QS) and Parti Québécois (PQ), as well as an independent member. There are 25 official political parties in Quebec.[159]
Quebec has a network of three offices for representing itself and defending its interests within Canada: one in Moncton for all provinces east, one in Toronto for all provinces west, and one in Ottawa for the federal government. These offices' mandate is to ensure an institutional presence of the Government of Quebec near other Canadian governments.[160][161]
Quebec's territory is divided into 17 administrative regions as follows:[162][163]

The province also has the following divisions:
For municipal purposes, Quebec is composed of:
Quebec's constitution is enshrined in a series of social and cultural traditions that are defined in a set of judicial judgments and legislative documents, including the Loi sur l'Assemblée Nationale ("Law on the National Assembly"), the Loi sur l'éxecutif ("Law on the Executive"), and the Loi électorale du Québec ("Electoral Law of Quebec").[166] Other notable examples include the Charter of Human Rights and Freedoms, the Charter of the French language, and the Civil Code of Quebec.[167]
Quebec's international policy is founded upon the Gérin-Lajoie doctrine,[168] formulated in 1965. While Quebec's Ministry of International Relations coordinates international policy, Quebec's general delegations are the main interlocutors in foreign countries. Quebec is the only Canadian province that has set up a ministry to exclusively embody the state's powers for international relations.[169]
Since 2006, Quebec has adopted a green plan to meet the objectives of the Kyoto Protocol regarding climate change.[170] The Ministry of Sustainable Development, Environment, and Fight Against Climate Change (MELCC) is the primary entity responsible for the application of environmental policy. The Société des établissements de plein air du Québec (SEPAQ) is the main body responsible for the management of national parks and wildlife reserves.[171] Nearly 500,000 people took part in a climate protest on the streets of Montreal in 2019.[172]
Agriculture in Quebec has been subject to agricultural zoning regulations since 1978.[173] Faced with the problem of expanding urban sprawl, agricultural zones were created to ensure the protection of fertile land, which make up 2% of Quebec's total area. Quebec's forests are essentially public property. The calculation of annual cutting possibilities is the responsibility of the Bureau du forestier en chef.[174] The Union des producteurs agricoles (UPA) seeks to protect the interests of its members, including forestry workers, and works jointly with the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food (MAPAQ) and the Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources.
The Ministère de l'Emploi et de la Solidarité sociale du Québec has the mandate to oversee social and workforce developments through Emploi-Québec and its local employment centres (CLE).[175] This ministry is also responsible for managing the Régime québécois d'assurance parentale (QPIP) as well as last-resort financial support for people in need. The Commission des normes, de l'équité, de la santé et de la sécurité du travail (CNESST) is the main body responsible for labour laws in Quebec[176] and for enforcing agreements concluded between unions of employees and their employers.[177]
Revenu Québec is the body responsible for collecting taxes. It takes its revenue through a progressive income tax, a 9.975% sales tax,[178] various other provincial taxes (ex. carbon, corporate and capital gains taxes), equalization payments, transfer payments from other provinces, and direct payments.[179] By some measures Quebec residents are the most taxed;[180] a 2012 study indicated that "Quebec companies pay 26 per cent more in taxes than the Canadian average".[181]
Quebec's immigration philosophy is based on the principles of pluralism and interculturalism.The Ministère de l'Immigration et des Communautés culturelles du Québec is responsible for the selection and integration of immigrants.[182] Programs favour immigrants who know French, have a low risk of becoming criminals and have in-demand skills.
Quebec's health and social services network is administered by the Ministry of Health and Social Services. It is composed of 95 réseaux locaux de services (RLS; 'local service networks') and 18 agences de la santé et des services sociaux (ASSS; 'health and social services agencies'). Quebec's health system is supported by the Régie de l'assurance maladie du Québec (RAMQ) which works to maintain the accessibility of services for all citizens of Quebec.[183]
The Ministère de la Famille et des Aînés du Québec operate centres de la petite enfance (CPEs; 'centres for young children'). Quebec's education system is administered by the Ministry of Education and Higher Education (primary and secondary schools), the Ministère de l'Enseignement supérieur (CEGEP) and the Conseil supérieure de l'Education du Québec (universities and colleges).[184] In 2012, the annual cost for postsecondary tuition was CA$2,168 (€1,700)—less than half of Canada's average tuition. Part of the reason for this is that tuition fees were frozen to a relatively low level when CEGEPS were created during the Quiet Revolution. When Jean Charest's government decided in 2012 to sharply increase university fees, students protests erupted.[185] Because of these protests, Quebec's tuition fees remain relatively low.
Quebec's closest international partner is the United States, with which it shares a long and positive history. Products of American culture like songs, movies, fashion and food strongly affect Québécois culture.
Quebec has a historied relationship with France, as Quebec was a part of the French Empire and both regions share a language. The Fédération France-Québec and the Francophonie are a few of the tools used for relations between Quebec and France. In Paris, a place du Québec was inaugurated in 1980.[186] Quebec also has a historied relationship with the United Kingdom, having been a part of the British Empire. Quebec and the UK share the same head of state, King Charles III.
Quebec has a network of 32 offices in 18 countries. These offices serve the purpose of representing Quebec in foreign countries and are overseen by Quebec's Ministry of International Relations. Quebec, like other Canadian provinces, also maintains representatives in some Canadian embassies and consulates general. As of 2019[update], the Government of Quebec had delegates-general (agents-general) in Brussels, London, Mexico City, Munich, New York City, Paris and Tokyo; delegates to Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, and Rome; and offices headed by directors offering more limited services in Barcelona, Beijing, Dakar, Hong Kong, Mumbai, São Paulo, Shanghai, Stockholm, and Washington. In addition, there are the equivalent of honorary consuls, titled antennes, in Berlin, Philadelphia, Qingdao, Seoul, and Silicon Valley.
Quebec also has a representative to UNESCO and participates in the Organization of American States.[187] Quebec is a member of the Assemblée parlementaire de la Francophonie and of the Organisation internationale de la francophonie.

Quebec law is the shared responsibility of the federal and provincial government. The federal government is responsible for criminal law, foreign affairs and laws relating to the regulation of Canadian commerce, interprovincial transportation, and telecommunications.[188] The provincial government is responsible for private law, the administration of justice, and several social domains, such as social assistance, healthcare, education, and natural resources.[188]
Quebec law is influenced by two judicial traditions (civil law and common law) and four classic sources of law (legislation, case law, doctrine and customary law).[189] Private law in Quebec affects all relationships between individuals (natural or juridical persons) and is largely under the jurisdiction of the Parliament of Quebec. The Parliament of Canada also influences Quebec private law, in particular through its power over banks, bankruptcy, marriage, divorce and maritime law.[190] The Droit civil du Québec is the primary component of Quebec's private law and is codified in the Civil Code of Quebec.[191] Public law in Quebec is largely derived from the common law tradition.[192] Quebec constitutional law governs the rules surrounding the Quebec government, the Parliament of Quebec and Quebec's courts. Quebec administrative law governs relations between individuals and the Quebec public administration. Quebec also has some limited jurisdiction over criminal law. Finally, Quebec, like the federal government, has tax law power.[193] Certain portions of Quebec law are considered mixed. This is the case, for example, with human rights and freedoms which are governed by the Quebec Charter of Human Rights and Freedoms, a Charter which applies to both government and citizens.[194][195]
English is not an official language in Quebec law.[196] However, both English and French are required by the Constitution Act, 1867 for the enactment of laws and regulations, and any person may use English or French in the National Assembly and the courts. The books and records of the National Assembly must also be kept in both languages.[197][198]
Although Quebec is a civil law jurisdiction, it does not follow the pattern of other civil law systems which have court systems divided by subject matter. Instead, the court system follows the English model of unitary courts of general jurisdiction. The provincial courts have jurisdiction to decide matters under provincial law as well as federal law, including civil, criminal and constitutional matters.[199] The major exception to the principle of general jurisdiction is that the Federal Court and Federal Court of Appeal have exclusive jurisdiction over some areas of federal law, such as review of federal administrative bodies, federal taxes, and matters relating to national security.[200]
The Quebec courts are organized in a pyramid. At the bottom, there are the municipal courts, the Professions Tribunal, the Human Rights Tribunal, and administrative tribunals. Decisions of those bodies can be reviewed by the two trial courts, the Court of Quebec the Superior Court of Quebec. The Court of Quebec is the main criminal trial court, and also a court for small civil claims. The Superior Court is a trial court of general jurisdiction, in both criminal and civil matters. The decisions of those courts can be appealed to the Quebec Court of Appeal. Finally, if the case is of great importance, it may be appealed to the Supreme Court of Canada.
The Court of Appeal serves two purposes. First, it is the general court of appeal for all legal issues from the lower courts. It hears appeals from the trial decisions of the Superior Court and the Quebec Court. It also can hear appeals from decisions rendered by those two courts on appeals or judicial review matters relating to the municipal courts and administrative tribunals.[201] Second, but much more rarely, the Court of Appeal possesses the power to respond to reference questions posed to it by the Quebec Cabinet. The Court of Appeal renders more than 1,500 judgments per year.[202]
The Sûreté du Québec is the main police force of Quebec. The Sûreté du Québec can also serve a support and coordination role with other police forces, such as with municipal police forces or with the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP).[203][204] The RCMP has the power to enforce certain federal laws in Quebec. However, given the existence of the Sûreté du Québec, its role is more limited than in the other provinces.[205]
Municipal police, such as the Service de police de la Ville de Montréal and the Service de police de la Ville de Québec, are responsible for law enforcement in their municipalities. The Sûreté du Québec fulfils the role of municipal police in the 1038 municipalities that do not have a municipal police force.[206] The Indigenous communities of Quebec have their own police forces.[207]
For offences against provincial or federal laws in Quebec (including the Criminal Code), the Director of Criminal and Penal Prosecutions is responsible for prosecuting offenders in court through Crown attorneys. The Department of Justice of Canada also has the power to prosecute offenders, but only for offences against specific federal laws (ex. selling narcotics). Quebec is responsible for operating the prison system for sentences of less than two years, and the federal government operates penitentiaries for sentences of two years or more.[208]

In the 2021 census, Quebec's population was determined to be 8,501,833, a 4.1% change from its 2016 population of 8,164,361. With a land area of 1,356,625.27 km2 (523,795.95 sq mi), it had a population density of 6.0/km2 (15.6/sq mi) in 2016. Quebec accounts for a little under 23% of the Canadian population. The most populated cities in Quebec are Montreal (1,762,976), Quebec City (538,738), Laval (431,208), and Gatineau (281,501).[209]
In 2016, Quebec's median age was 41.2 years. As of 2020, 20.8% of the population were younger than 20, 59.5% were aged between 20 and 64, and 19.7% were 65 or older. In 2019, Quebec witnessed an increase in the number of births compared to the year before (84,200 vs 83,840) and had a total fertility rate of about 1.6 children born per woman. As of 2020, the average life expectancy was 82.3 years. Quebec in 2019 registered the highest rate of population growth since 1972, with an increase of 110,000 people, mostly because of the arrival of a high number of immigrants. As of 2019, most international immigrants came from China, India or France.[210] In 2016, 30% of the population possessed a postsecondary degree or diploma. Most residents, particularly couples, are property owners. In 2016, 80% of both property owners and renters considered their housing to be "unaffordable".[211] In the 2021 Canadian census, 29.3% of Quebec's population stated their ancestry was of Canadian origin and 21.1% stated their ancestry was of French origin.[212] As of 2021, 18% of Quebec's population were visible minorities.[213]

According to the 2021 census, the most commonly cited religions in Quebec were:[214]
The Roman Catholic Church has long occupied a central and integral place in Quebec society since the foundation of Quebec City in 1608. However, since the Quiet Revolution, which secularized Quebec, irreligion has been growing significantly.[215]
Asian or Middle Eastern religions were not present before the 20th century. They started establishing a small presence following the passing of the Immigration Act of 1962. Islam in particular has grown rapidly since the 1990s due to high immigration levels. It went from 44,930 followers (0.6% of the population) in 1991 to 421,715 followers (5.1%) in 2021.[216][217]
The oldest parish church in North America is the Cathedral-Basilica of Notre-Dame de Québec. Its construction began in 1647, when it was known under the name Notre-Dame-de-la-Paix, and it was finished in 1664.[218] The most frequented place of worship in Quebec is the Basilica of Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré. This basilica welcomes millions of visitors each year. Saint Joseph's Oratory is the largest place of worship in the world dedicated to Saint Joseph. Many pilgrimages include places such as Saint Benedict Abbey, Sanctuaire Notre-Dame-du-Cap, Notre-Dame de Montréal Basilica, Marie-Reine-du-Monde de Montréal Basilica-Cathedral, Saint-Michel Basilica-Cathedral, and Saint-Patrick's Basilica. Another important place of worship in Quebec is the Anglican Holy Trinity Cathedral, which was erected between 1800 and 1804. It was the first Anglican cathedral built outside the British Isles.[219]

|
Linguistic map of the province of Quebec (source: Statistics Canada, 2006 census)
|
Quebec differs from other Canadian provinces in that French (Quebecois) is the only official and preponderant language, while English predominates in the rest of Canada.[220] French is the common language, understood and spoken by 94.4% of the population.[221][222] Québécois French is the local variant of the language. Canada is estimated to be home to roughly 30 regional French accents,[223][224] 17 of which can be found in Quebec.[225] The Office québécois de la langue française oversees the application of linguistic policies respecting French on the territory, jointly with the Superior Council of the French Language and the Commission de toponymie du Québec. The foundation for these linguistic policies was created in 1968 by the Gendron Commission and they have been accompanied the Charter of the French language ("Bill 101") since 1977. The policies are in effect to protect Quebec from being assimilated by its English-speaking neighbours (the rest of Canada and the United States)[226][227] and were also created to rectify historical injustice between the Francophone majority and Anglophone minority, the latter of which were favoured since Quebec was a colony of the British Empire.[228]
Quebec is the only Canadian province whose population is mainly Francophone, meaning that French is their native language. In the 2011 Census, 6,102,210 people (78.1% of the population) recorded French as their sole native language and 6,249,085 (80.0%) recorded that they spoke French most often at home.[229]
People with English as their native language, called Anglo-Quebecers, constitute the second largest linguistic group in Quebec. In 2011, English was the mother tongue of nearly 650,000 Quebecers (8% of the population).[230] Anglo-Quebecers reside mainly in the west of the island of Montreal (West Island), downtown Montreal and the Pontiac.
Three families of Indigenous languages encompassing eleven languages exist in Quebec: the Algonquian language family (Abenaki, Algonquin, Maliseet-passamaquoddy, Mi'kmaq, and the linguistic continuum of Atikamekw, Cree, Innu-aimun, and Naskapi), the Inuit–Aleut language family (Nunavimmiutitut, an Inuktitut dialect spoken by the Inuit of Nord-du-Québec), and the Iroquoian language family (Mohawk and Wendat). In the 2016 census, 50,895 people said they knew at least one Indigenous language[231] and 45,570 people declared having an Indigenous language as their mother tongue.[232] In Quebec, most Indigenous languages are transmitted quite well from one generation to the next with a mother tongue retention rate of 92%.[233]
As of the 2016 census, the most common immigrant languages claimed as a native language were Arabic (2.5% of the total population), Spanish (1.9%), Italian (1.4%), Creole languages (mainly Haitian Creole) (0.8%), and Mandarin (0.6%).[234]
As of the 2021 Canadian Census, the ten most spoken languages in the province were French (spoken by 7,786,735 people, or 93.72% of the population), English (4,317,180 or 51.96%), Spanish (453,905 or 5.46%), Arabic (343,675 or 4.14%), Italian (168,040 or 2.02%), Haitian Creole (118,010 or 1.42%), Mandarin (80,520 or 0.97%), Portuguese (65,605 or 0.8%), Russian (55,485 or 0.7%), and Greek (50,375 or 0.6%).[235] The question on knowledge of languages allows for multiple responses.

In 2021, the Indigenous population of Quebec numbered 205,010 (2.5% of the population), including 15,800 Inuit, 116,550 First Nations people, and 61,010 Métis.[236] There is an undercount, as some Indian bands regularly refuse to participate in Canadian censuses. In 2016, the Mohawk reserves of Kahnawake and Doncaster 17 along with the Indian settlement of Kanesatake and Lac-Rapide, a reserve of the Algonquins of Barriere Lake, were not counted.[237]
The Inuit of Quebec live mainly in Nunavik in Nord-du-Québec. They make up the majority of the population living north of the 55th parallel. There are ten First Nations ethnic groups in Quebec: the Abenaki, the Algonquin, the Attikamek, the Cree, the Wolastoqiyik, the Mi'kmaq, the Innu, the Naskapis, the Huron-Wendat and the Mohawks. The Mohawks were once part of the Iroquois Confederacy. Aboriginal rights were enunciated in the Indian Act and adopted at the end of the 19th century. This act confines First Nations within the reserves created for them. The Indian Act is still in effect today.[238] In 1975, the Cree, Inuit and the Quebec government agreed to an agreement called the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement that would extended indigenous rights beyond reserves, and to over two-thirds of Quebec's territory. Because this extension was enacted without the participation of the federal government, the extended indigenous rights only exist in Quebec. In 1978, the Naskapis joined the agreement when the Northeastern Quebec Agreement was signed. Discussions have been underway with the Montagnais of the Côte-Nord and Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean for the potential creation of a similar autonomy in two new distinct territories that would be called Innu Assi and Nitassinan.[239]
A few political institutions have also been created over time:
The subject of Acadians in Quebec is an important one as more than a million people in Quebec are of Acadian descent, with roughly 4.8 million people possessing one or multiple Acadian ancestors in their genealogy tree, because a large number of Acadians had fled Acadia to take refuge in Quebec during the Great Upheaval. Furthermore, more than a million people have a patronym of Acadian origin.[243][244][245][246]
Quebec houses Acadian communities. Acadians mainly live on the Magdalen Islands and in Gaspesia, but about thirty other communities are present elsewhere in Quebec, mostly in the Côte-Nord and Centre-du-Québec regions. An Acadian community in Quebec can be called a "Cadie", "Petite Cadie" or "Cadien".[247]
Quebec has an advanced, market-based, and open economy. In 2022, its gross domestic product (GDP) was US$50,000 per person at purchasing power parity.[248] The economy of Quebec is the 46th largest in the world behind Chile and 29th for GDP per person.[249][250] Quebec represents 19% of the GDP of Canada. The provincial debt-to-GDP ratio peaked at 51% in 2012–2013, and declined to 43% in 2021.[251]
Like most industrialized countries, the economy is based mainly on the services sector. Quebec's economy has traditionally been fuelled by abundant natural resources and a well-developed infrastructure, but has undergone significant change over the past decade.[252] Firmly grounded in the knowledge economy, Quebec has one of the highest growth rates of GDP in Canada. The knowledge sector represents about 31% of Quebec's GDP.[253] In 2011, Quebec experienced faster growth of its research-and-development (R&D) spending than other Canadian provinces.[254] Quebec's spending in R&D in 2011 was equal to 2.63% of GDP, above the European Union average of 1.8%.[255] The percentage spent on research and technology is the highest in Canada and higher than the averages for the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and the G7 countries.[256]
Some of the most important companies from Quebec are: Bombardier, Desjardins, the National Bank of Canada, the Jean Coutu Group, Transcontinental média, Quebecor, the Métro Inc. food retailers, Hydro-Québec, the Société des alcools du Québec, the Bank of Montreal, Saputo, the Cirque du Soleil, the Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec, the Normandin restaurants, and Vidéotron.

Thanks to the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), Quebec had, as of 2009[update], experienced an increase in its exports and in its ability to compete on the international market. International exchanges contribute to the strength of the Quebec economy.[257] NAFTA is especially advantageous as it gives Quebec, among other things, access to a market of 130 million consumers within a radius of 1,000 kilometres.
In 2008, Quebec's exports to other provinces in Canada and abroad totalled 157.3 billion CND$, or 51.8% of Quebec's gross domestic product (GDP). Of this total, 60.4% were international exports, and 39.6% were interprovincial exports. The breakdown by destination of international merchandise exports is: United States (72.2%), Europe (14.4%), Asia (5.1%), Middle East (2.7%), Central America (2.3%), South America (1.9%), Africa (0.8%) and Oceania (0.7%).[257]
In 2008, Quebec imported $178 billion worth of goods and services, or 58.6% of its GDP. Of this total, 62.9% of goods were imported from international markets, while 37.1% of goods were interprovincial imports. The breakdown by origin of international merchandise imports is as follows: United States (31.1%), Europe (28.7%), Asia (17.1%), Africa (11.7%), South America (4.5%), Central America (3.7%), Middle East (1.3%) and Oceania (0.7%).[257]

Quebec produces most of Canada's hydroelectricity and is the second biggest hydroelectricity producer in the world (2019).[258] Because of this, Quebec has been described as a potential clean energy superpower.[259] In 2019, Quebec's electricity production amounted to 214 terawatt-hours (TWh), 95% of which comes from hydroelectric power stations, and 4.7% of which come from wind energy. The public company Hydro-Québec occupies a dominant position in the production, transmission and distribution of electricity in Quebec. Hydro-Québec operates 63 hydroelectric power stations and 28 large reservoirs.[260] Because of the remoteness of Hydro-Québec's TransÉnergie division, it operates the largest electricity transmission network in North America. Quebec stands out for its use of renewable energy. In 2008, electricity ranked as the main form of energy used in Quebec (41.6%), followed by oil (38.2%) and natural gas (10.7%).[261] In 2017, 47% of all energy came from renewable sources.[262] The Quebec government's energy policy seeks to build, by 2030, a low carbon economy.
Quebec ranks among the top ten areas to do business in mining in the world.[263] In 2011, the mining industry accounted for 6.3% of Quebec's GDP[264] and it employed about 50,000 people in 158 companies.[265] It has around 30 mines, 158 exploration companies and 15 primary processing industries. While many metallic and industrial minerals are exploited, the main ones are gold, iron, copper and zinc. Others include: titanium, asbestos, silver, magnesium and nickel, among many others.[266] Quebec is also as a major source of diamonds.[267] Since 2002, Quebec has seen an increase in its mineral explorations. In 2003, the value of mineral exploitation reached $3.7 billion.[268]
The agri-food industry plays an important role in the economy of Quebec, with meat and dairy products being the two main sectors. It accounts for 8% of the Quebec's GDP and generate $19.2 billion. In 2010, this industry generated 487,000 jobs in agriculture, fisheries, manufacturing of food, beverages and tobacco and food distribution.[269]

In 2021, Quebec's aerospace industry employed 35,000 people and its sales totalled C$15.2 billion - the world's 6th largest.[270] Many aerospace companies are active here, including CMC Electronics, Bombardier, Pratt & Whitney Canada, Héroux-Devtek, Rolls-Royce, General Electric, Bell Textron, L3Harris, Safran, SONACA, CAE Inc., and Airbus, among others. Montreal is globally considered one of the aerospace industry's great centres, and several international aviation organisations seat here.[271] Both Aéro Montréal and the CRIAQ were created to assist aerospace companies.[272][273]
The pulp and paper industry accounted for 3.1% of Quebec's GDP in 2007 [274] and generated annual shipments valued at more than $14 billion.[275] This industry employs 68,000 people in several regions of Quebec.[276] It is also the main -and in some circumstances only- source of manufacturing activity in more than 250 municipalities in the province. The forest industry has slowed in recent years because of the softwood lumber dispute.[277] In 2020, this industry represented 8% of Quebec's exports.[278]
As Quebec has few significant deposits of fossil fuels,[279] all hydrocarbons are imported. Refiners' sourcing strategies have varied over time and have depended on market conditions. In the 1990s, Quebec purchased much of its oil from the North Sea. Since 2015, it now consumes almost exclusively the crude produced in western Canada and the United States.[280] Quebec's two active refineries have a total capacity of 402,000 barrels per day, greater than local needs which stood at 365,000 barrels per day in 2018.[279]
Thanks to hydroelectricity, Quebec is the world's fourth largest aluminum producer and creates 90% of Canadian aluminum. Three companies make aluminum here: Rio Tinto, Alcoa and Aluminium Alouette. Their 9 alumineries produce 2,9 million tons of aluminum annually and employ 30,000 workers.[281]
The finance and insurance sector employs more than 168,000 people. Of this number, 78,000 are employed by the banking sector, 53,000 by the insurance sector and 20,000 by the securities and investment sector.[282] The Bank of Montreal, founded in 1817 in Montreal, was Quebec's first bank but, like many other large banks, its central branch is now in Toronto. Several banks remain based in Quebec National Bank of Canada, the Desjardins Group and the Laurentian Bank.

The tourism industry is a major sector in Quebec. The Ministry of Tourism ensures the development of this industry under the commercial name "Bonjour Québec".[283] Quebec is the second most important province for tourism in Canada, receiving 21.5% of tourists' spending (2021).[284] The industry provides employment to over 400,000 people.[285] These employees work in the more than 29,000 tourism-related businesses in Quebec, most of which are restaurants or hotels. 70% of tourism-related businesses are located in or close to Montreal or Quebec City. It is estimated that, in 2010, Quebec welcomed 25.8 million tourists. Of these, 76.1% came from Quebec, 12.2% from the rest of Canada, 7.7% from the United States and 4.1% from other countries. Annually, tourists spend more than $6.7 billion in Quebec's tourism industry.[286]
Approximately 1.1 million Quebecers work in the field of science and technology.[287] In 2007, the Government of Quebec launched the Stratégie québécoise de la recherche et de l'innovation (SQRI) aiming to promote development through research, science and technology. The government hoped to create a strong culture of innovation in Quebec for the next decades and to create a sustainable economy.[288]
Quebec's IT sector has 7,600 businesses and employs 140,000 people.[289][290][291] Its most developed sectors are telecommunications, multimedia and video game software, computer services, microelectronics, and the components sector. There are currently 115 telecommunications companies established in the province, including Motorola, Ericsson and Mitec.[292] The multimedia and video game sector has been growing fast since the early 2000s. The Digital Alliance, which claims 191 active members in video games, online education, mobility and Internet services, estimates the annual revenue of the sector at $827 million in 2014.[293] The microelectronics sector is made up of more than 100 companies employing 13,000 people. Computer services, software development, and consulting engineering employ 60,000 skilled workers. While the largest IT employers are CMC Electronics, IBM, and Matrox, many other tech companies are present here, including Ubisoft, Electronic Arts, Microids, Strategy First, Eidos, Activision, A2M, Frima Studio, etc.[294]
Montreal is ranked fourth in North America for the number of jobs in the pharmaceutical sector.[295][296]
The education system of Quebec, administered by the government of Quebec's Ministry of Education and Higher Education, differs from those of other Canadian provinces. The province has five levels of education: first preschool, then primary school, then secondary school; then CEGEP (see College education in Quebec); and finally university or college. Attached to these levels are the options to also attend professional development opportunities, classes for adults, and continuing education. For every level of teaching, there exists a public network and private network: the public network is financed by taxes while the private options must be paid for by the student. In 2020, school boards were replaced by school service centres.[297]
All universities in Quebec exist by virtue of laws adopted by the National Assembly of Quebec in 1967 during the Quiet Revolution. Their financing mostly comes from public taxes, but the laws under which they operate grants them more autonomy than other levels of education.[298]

Quebec is considered one of world leaders in fundamental scientific research, having produced ten Nobel laureates in either physics, chemistry, or medicine.[299] It is also considered one of the world leaders in sectors such as aerospace, information technology, biotechnology and pharmaceuticals, and therefore plays a significant role in the world's scientific and technological communities.[300] Between 2000 and 2011, Quebec had over 9,469 scientific publications in biomedical research and engineering.[301] The contribution of Quebec in science and technology represented approximately 1% of the research worldwide between the 1980s and 2009.[302]

The province is one of the world leaders in the field of space science and contributed to important discoveries in this field.[303] The Canadian Space Agency was established in Quebec due to its major role in this research field. A total of four Quebecers have been in space since the creation of the CSA: Marc Garneau, Julie Payette, and David Saint-Jacques as CSA astronauts, plus Guy Laliberté as a private citizen who paid for his trip. Quebec has also contributed to the creation of some Canadian artificial satellites including SCISAT-1, ISIS, Radarsat-1 and Radarsat-2.[304][305][306]
Quebec ranks among the world leaders in the field of life science.[295] Quebec has more than 450 biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies which together employ more than 25,000 people and 10,000 highly qualified researchers.[295]

Development and security of land transportation in Canada are provided by Transports Québec.[307] Other organizations, such as the Canadian Coast Guard and Nav Canada, provide the same service for the sea and air transportation. The Commission des transports du Québec works with the freight carriers and the public transport.
The réseau routier québécois (Quebec road network) is managed by the Société de l'assurance automobile du Québec (SAAQ; Quebec Automobile Insurance Corporation) and consists of about 185,000 km (115,000 mi) of highways and national, regional, local, collector and forest roads. In addition, Quebec has almost 12,000 bridges, tunnels, retaining walls, culverts and other structures[308] such as the Quebec Bridge, the Laviolette Bridge and the Louis-Hippolyte Lafontaine Bridge–Tunnel.
In the waters of the Saint Lawrence there are eight deep-water ports for the transhipment of goods. In 2003, 3886 cargo and 9.7 million tonnes of goods transited the Quebec portion of the Saint Lawrence Seaway.[309]
Concerning rail transport, Quebec has 6,678 km (4,150 mi) of railways[310] integrated in the large North American network. Although primarily intended for the transport of goods through companies such as the Canadian National (CN) and the Canadian Pacific (CP), the Quebec railway network is also used by inter-city passengers via Via Rail Canada and Amtrak. In April 2012, plans were unveiled for the construction of an 800 km (497 mi) railway running north from Sept-Îles, to support mining and other resource extraction in the Labrador Trough.[311]
Quebec's air network includes 43 airports that offer scheduled services on a daily basis.[309] In addition, the Government of Quebec owns airports and heliports to increase the accessibility of local services to communities in the Basse-Côte-Nord and northern regions.[312]
Various other transport networks crisscross the province of Quebec, including hiking trails, snowmobile trails and bike paths. The Green Road is the largest at nearly 4,000 km (2,500 mi) in length.[313]
Quebec has a health policy that emphasizes prevention, is based on the analysis of health-related data, and evolves with the needs of the population. Similar to other developed economies, the public health policies implemented in Quebec have extended the life expectancy of its population since the mid-20th century.[314]
Health and social services are part of the same administration. The Quebec health system is also public, which means that the government acts as the main insurer and administrator, that funding is provided by general taxation, and that patients have access to care regardless of their income level.
There are 34 health establishments in Quebec, 22 of which are an Integrated Health and Social Services Centre (CISSS). They ensure the distribution of different services on the territories they are assigned to. Quebec has approximately 140 hospitals for general or specialised care (CHSGS). Quebec also has other types of establishments in its healthcare system, such as Centre local de services communautaires (CLSC), Centre d'hébergement et de soins de longue durée (CHSLD), Centre de réadaptation and Centre de protection de l'enfance et de la jeunesse. Finally, there are private healthcare establishments (paid for directly by the patient) like Groupe de médecine de famille, pharmacies, private clinics, dentists, community organisations and retirement homes.[315]
A 2021 Ipsos poll found that 85% of Quebecers agree that their health care system is too bureaucratic to respond to the needs of the population[316] and in 2023 found that less than half of Quebecers are satisfied with the provincial health care system.[317]
In 2021, 59.9% of Quebec's residents were property owners.[318] In 2019, among property owners, 34% were couples with kids, 33% were couples without children, 22% lived alone, 8% were single parents, and 3% were something else. Among renters, 16% were couples with kids, 13% were couples without children, 51% lived alone, 13% were single parents, and 7% were something else.[211]
Since the 1980s, the average price of a single-family home has doubled every 10 years, going from $48,715 in 1980 to $424,844 in 2021. Since the average salary did not follow these increases, Quebec homes are 10 times more expensive than they were 40 years ago.[319] In 2022, the cities with the most severe housing shortages were Granby, with a vacancy rate of 0,1%, followed by Marieville (0,1%), Rimouski (0,2%), Drummondville (0,2%) and Rouyn-Noranda (0,3%).[320]
Quebec has developed its own unique culture from its historic New France roots. Its culture also symbolizes a distinct perspective: being a French-speaking nation surrounded by a bigger English-speaking culture.
The Quartier Latin (English: Latin Quarter) of Montreal, and Vieux-Québec (English: Old Quebec) in Quebec City are two hubs of metropolitan cultural activity. Life in the cafés and "terrasses" (outdoor restaurant terraces) reveals a Latin influence in Quebec's culture, with the théâtre Saint-Denis in Montreal and the Capitole de Québec theatre in Quebec City being among the principal attractions.
A number of governmental and non-government organizations support cultural activity in Quebec. The Conseil des arts et des lettres du Québec (CALQ) is an initiative of the Ministry of Culture and Communications (Quebec). It supports creation, innovation, production, and international exhibits for all cultural fields of Quebec. The Société de développement des entreprises culturelles (SODEC) works to promote and fund individuals working in the cultural industry. The Prix du Québec is an award given by the government to confer the highest distinction and honour to individuals demonstrating exceptional achievement in their respective cultural field. Other awards include the Athanase David Awards (Literature), Félix Awards (Music), Gémeaux Awards (Television and film), Jutra Awards (Cinema), Masques Awards (Theatre), Olivier Guimond Awards (Humour) and the Opus Awards (Concert music).
Traditional music is imbued with many dances, such as the jig, the quadrille, the reel and line dancing. Traditional instruments include harmonica, fiddle, spoons, jaw harp and accordion. The First Nations and the Inuit of Quebec also have their own traditional music. Quebec's most popular artists of the last century include the singers Félix Leclerc, Gilles Vigneault, Kate and Anna McGarrigle and Céline Dion.[321] The Association québécoise de l'industrie du disque, du spectacle et de la vidéo (ADISQ) was created in 1978 to promote the music industry in Quebec.[322] The Orchestre symphonique de Québec and the Montreal Symphony Orchestra are respectively associated with the Opéra de Québec and the Opéra de Montreal whose performances are presented at the Grand Théâtre de Québec and at Place des Arts. The Ballets Jazz de Montreal, the Grands Ballets and La La La Human Steps are three important professional troupes of contemporary dance.
Among the theatre troupes are the Compagnie Jean-Duceppe, the Théâtre La Rubrique, and the Théâtre Le Grenier. In addition to the network of cultural centres in Quebec,[323] the venues include the Monument-National and the Rideau Vert (green curtain) Theatre in Montreal, and the Trident Theatre in Quebec City. The National Theatre School of Canada and the Conservatoire de musique et d'art dramatique du Québec form the future players.

Several circus troupes were created in recent decades, the most important being the Cirque du Soleil.[324] Among these troops are contemporary, travelling and on-horseback circuses, such as Les 7 Doigts de la Main, Cirque Éloize, Cavalia, Kosmogonia, Saka and Cirque Akya.[325] The National Circus School and the École de cirque de Québec were created to train future Contemporary circus artists. Tohu, la Cité des Arts du Cirque was founded in 2004 to disseminate the circus arts.[326]
Comedy is a vast cultural sector. Quebec has created and is home to several different comedy festivals, including the Just for Laughs festival in Montreal, as well as the Grand Rire festivals of Quebec, Gatineau and Sherbrooke.[327] The Association des professionnels de l'industrie de l'humour (APIH) is the main organization for the promotion and development of the cultural sector of humour in Quebec and the National School of Humour, created in 1988, trains future humorists in Quebec.
The Cinémathèque québécoise has a mandate to promote the film and television heritage of Quebec. The National Film Board of Canada (NFB), a federal Crown corporation, provides for the same mission in Canada. The Association of Film and Television in Quebec (APFTQ) promotes independent production in film and television.[328] While the Association of Producers and Directors of Quebec (APDQ) represents the business of filmmaking and television, the Association of Community Radio Broadcasters of Quebec (ARCQ) (French acronym) represents the independent radio stations.[329] Several movie theatres across Quebec ensure the dissemination of Quebec cinema. With its cinematic installations, such as the Cité du cinéma and Mel's studios, the city of Montreal is home to the filming of various productions.[330] The state corporation Télé-Québec, the federal Crown corporation CBC, general and specialized private channels, networks, independent and community radio stations broadcast the various Quebec téléromans, the national and regional news, and other programming.[331][332] Les Rendez-vous du cinéma québécois is a festival surrounding the ceremony of the Jutra Awards Night that rewards work and personalities of Quebec cinema.[333] The Artis and the Gemini Awards gala recognize the personalities of television and radio industry in Quebec and French Canada. The Film Festival of the 3 Americas, the Festival of International Short Film, the World Film Festival and the Festival of New Cinema are other annual events surrounding the film industry in Quebec.
Popular comedy shows include Cré Basile, Le zoo du Capitaine Bonhomme, Lundi des Ha! Ha !, Démons du midi, La petite vie, Les Bougon, and Le sketch show. There are also many comedy and cartoon shows created for children, such as La boîte à surprise, Bobino, Le pirate Maboule, Fanfreluche, La Ribouldingue, Les 100 Tours de Centour, Patofville, Passe-Partout, Robin et Stella, Iniminimagimo, Vazimolo, Télé-Pirate, Bibi et Geneviève, Watatatow, Caillou, Cornemuse, Macaroni tout garni, Toc toc toc, Ramdam, and Tactik.
In the realm of literature and international publishing, the Québec Édition group is a committee created by the National Association of Book Editors dedicated to the international influence of French-language publishings from Quebec and Canada.[334]

Quebec's French-speaking populace has the second largest body of folktales in Canada (the first being First Nations).[335] When the early settlers arrived from France in the 17th century, they brought with them popular tales from their homeland, which were adapted to the local context. Many were passed on through generations by raconteurs, or storytellers.[336] Almost all of the stories native to Quebec were influenced by Christian dogma and superstitions. The Devil, for instance, appears often as either a person, an animal or monster, or indirectly through Demonic acts.[337] Various tales and stories are told through oral tradition, such as, among many others, the legends of the Bogeyman, the Chasse-galerie, the Black Horse of Trois-Pistoles, the Complainte de Cadieux, the Corriveau, the dancing devil of Saint-Ambroise, the Giant Beaupré, the monsters of the lakes Pohénégamook and Memphremagog, of Quebec Bridge (called the Devil's Bridge), the Rocher Percé and of Rose Latulipe, for example.[338]
From New France, Quebec literature was first developed in the travel accounts of explorers. The Moulin à paroles traces the great texts that have shaped the history of Quebec. The first to write the history of Quebec, since its discovery, was the historian François-Xavier Garneau. Many Quebec poets and prominent authors marked their era and today remain anchored in the collective imagination, like, among others, Philippe Aubert de Gaspé, Octave Crémazie, Honoré Beaugrand, Émile Nelligan, Lionel Groulx, Gabrielle Roy, Hubert Aquin, Michel Tremblay, Marie Laberge, Fred Pellerin and Gaston Miron. The regional novel from Quebec is called Terroir novel and is a literary tradition[339] specific to the province.
Popular French-language contemporary writers include Louis Caron, Suzanne Jacob, Yves Beauchemin, and Gilles Archambault. Well-known English-language writers from Quebec include Leonard Cohen, Mordecai Richler, and Neil Bissoondath.

The art of Quebec has developed around the specific characteristics of its landscapes and cultural, historical, social and political representations. The development of Quebec masterpieces in painting, printmaking and sculpture is marked by the contribution of artists such as Louis-Philippe Hébert, Cornelius Krieghoff, Alfred Laliberté, Marc-Aurèle Fortin, Marc-Aurèle de Foy Suzor-Coté, Jean Paul Lemieux, Clarence Gagnon, Adrien Dufresne, Alfred Pellan, Jean-Philippe Dallaire, Charles Daudelin, Arthur Villeneuve, Jean-Paul Riopelle, Paul-Émile Borduas and Marcelle Ferron.
The fine arts of Quebec are displayed at the Quebec National Museum of Fine Arts, the Montreal Museum of Contemporary Art, the Montreal Museum of Fine Arts, the Quebec Salon des métiers d'art and in many art galleries. The Montreal School of Fine Arts forms the painters, printmakers and sculptors of Quebec.

Quebec's architecture is characterized by its unique Canadien-style buildings as well as the juxtaposition of a variety of styles reflective of Quebec's history. When walking in any city or town, one can come across buildings with styles congruent to Classical, Neo-Gothic, Roman, Neo-Renaissance, Greek Revival, Neo-Classical, Québécois Neo-Classical, Victorian, Second Empire, Modern, Post-modern or Skyscrapers.
Canadien-style houses and barns were developed by the first settlers of New France along the banks of the Saint Lawrence River. These buildings are rectangular one-storey structures with an extremely tall and steep roof, sometimes almost twice as tall as the house below. Canadien-style churches also developed and served as landmarks while traversing rural Quebec.

Several sites, houses and historical works reflect the cultural heritage of Quebec, such as the Village Québécois d'Antan, the historical village of Val-Jalbert, the Fort Chambly, the national home of the Patriots, the Chicoutimi pulp mill (Pulperie de Chicoutimi), the Lachine Canal and the Victoria Bridge. As of December 2011, there are 198 National Historic Sites of Canada in Quebec.[341] These sites were designated as being of national historic significance.[342]
Various museums tell the cultural history of Quebec, like the Museum of Civilization, the Museum of French America, the McCord Museum or the Montreal Museum of Archaeology and History in Pointe-à-Callière, displaying artifacts, paintings and other remains from the past of Quebec. Notable schools include the Conservatoire de musique et d'art dramatique du Québec, the École nationale de théâtre du Canada and the École nationale de cirque. Notable public agencies to catalogue and further develop Quebec's culture include the Bibliothèque et Archives nationales du Québec, the Conseil des arts et des lettres du Québec and Télé-Québec. The Association Quebecoise des Loisirs Folkloriques is an organization committed to preserving and disseminating Quebec's folklore heritage.[343]

The traditional Quebecois cuisine descends from 16th-century French cuisine, the fur trade and a history of hunting. Quebec's cuisine has also been influenced by learning from First Nation, by English cuisine and by American cuisine. Quebec is most famous for its tourtière, pâté chinois, poutine, and St. Catherine's taffy among others. "Le temps des sucres" is a period during springtime when many Quebecers go to the sugar shack (cabane à sucre) for a traditional meal.
Quebec is the world's biggest maple syrup producer.[344] The province has a long history of producing maple syrup, and creating new maple-derived products. Other major food products include beer, wine (including ice wine and ice cider), and cheese.

Sports in Quebec constitutes an essential dimension of Quebec culture. Ice hockey remains the national sport. This sport was played for the first time on March 3, 1875, in Montreal and has been promoted over the years by numerous achievements, including the centenary of the Montreal Canadiens.[345] Other major sports include Canadian football with the Montreal Alouettes, soccer with Club de Foot Montréal, the Grand Prix du Canada Formula 1 racing with drivers such as Gilles Villeneuve and Jacques Villeneuve, and professional baseball with the former Montreal Expos. Quebec has hosted several major sporting events, including the 1976 Summer Olympics, the Fencing World Championships in 1967, track cycling in 1974, and the Transat Québec-Saint-Malo race created in 1984.
Quebec athletes have performed well at the Winter Olympics over recent years. They won 12 of Canada's 29 medals at the most recent Winter Olympics in Pyeongchang (2018); they won 12 of the 27 Canadian medals in Sochi (2014); and 9 of the 26 Canadian medals in Vancouver (2010).[346]
St-Jean-Baptiste Day is one of Quebec's biggest holidays. In 1977, the Quebec Parliament declared June 24, the day of La Saint-Jean-Baptiste, to be Quebec's National Holiday. La Saint-Jean-Baptiste, or La St-Jean, honours French Canada's patron saint, John the Baptist. On this day, the song "Gens du pays", by Gilles Vigneault, is often heard. The song À la claire fontaine[347] was the anthem of the New France, Patriots and French Canadian, then replaced by O Canada, but "Gens du pays" is preferred by many Quebecers to be the national anthem of Quebec.
National Patriots' Day, a statutory holiday in Quebec, is also a unique public holiday, which honours the patriotes with displays of the patriote flag, music, public speeches, and ceremonies.[348] Le Vieux de '37 ("The Old Man of '37"), an illustration by Henri Julien that depicts a patriot of this rebellion,[349] is sometimes added at the centre of Patriote flags. Moving Day is a tradition where leases terminate on July 1. This creates a social phenomenon where everyone seems to be moving out at the same time.[350]
Other distinct holiday traditions include the Réveillon, a giant feast and party which takes place during Christmas Eve and New Year's Eve and goes on until midnight. Traditional dishes like tourtière or cipâte are offered, and rigaudon, spoon or violin may be played.[351] Finally, April Fools' Day is called Poisson d'Avril ("April's Fish") because while pulling pranks is still important, there is another major tradition: sticking fish-shaped paper cutouts to people's backs without them noticing.[352]
In 1939, the government of Quebec unilaterally ratified its coat of arms to reflect Quebec's political history: French rule (gold lily on blue background), followed by British rule (lion on red background), followed by Canadian rule (maple leaves).[353] Je me souviens ("I remember") is an official part of the coat of arms and has been the official licence plate motto since 1978, replacing the previous motto: La belle province ("the beautiful province"), still used as a nickname for the province. The fleur-de-lis, one of Quebec's most common symbols, is an ancient symbol of the French monarchy. Finally, the Great Seal of Quebec is used to authenticate documents issued by the government of Quebec.
The first members of the Saint-Jean-Baptiste Society created the Carillon Sacré-Coeur flag, which consisted of a white cross on an azure background with white fleur-de-lis in each corner and a Sacred Heart surrounded by maple leaves in the centre; it was based on the French merchant flag flown by Champlain and the Flag of Carillon. The Carillon Sacré-Coeur and French merchant flag went on to be the major inspirations for creating Quebec's current flag in 1903, called the Fleurdelisé. The Fleurdelisé replaced the Union Jack on Quebec's Parliament Building on January 21, 1948.

Three new official emblems in were adopted in the late 20th century: the Snowy owl in 1987 to symbolize the whiteness of Quebec's semi-northern climate, the Yellow birch in 1993 for the variety of its uses and by its commercial value, and the Iris versicolor in 1999 to illustrate the cultural diversity of Quebec and the importance of water and wetlands for the balance of nature.[354][355]
The earliest immigrants to the Canadian prairies were French Canadians from Quebec. Many Franco-Albertans, Fransaskois and Franco-Manitobans are descended from them.
From the mid-1800s to the Great Depression, Quebec experienced the Grande Hémorragie ("Great Hemorrhaging"), a massive emigration of 900,000 people from Quebec to New England.[356] French Canadians often established themselves in Little Canadas in many industrial New England centres. Of the 900,000 Québécois who emigrated, about half returned.[357] Most of the descendants of those who stayed are now assimilated, though a few Franco-Americans remain, speaking New England French.
Some tried to slow the Grande Hémorragie by redirecting people north, which resulted in the founding of many regions in Quebec (ex. Saguenay-Lac-St-Jean, Val-d'Or) but also in Northeastern Ontario. The northeastern Franco-Ontarians of today, who live in Timmins, Hearst, Moosonee and Sault Sainte Marie, among others, are the descendants of emigrants from Quebec who worked in the mines of the area.[358]
In recent times, snowbirds often migrate to southern Florida during the winter, resulting in the emergence of temporary "Québécois regions," such as in Hollywood.[359]
Quebec is divided into 17 administrative regions which bring together 104 regional county municipalities (MRC) and several independent municipalities.
cite web: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)The ecological classification of Quebec territory consists of mapping and description of ecological units at various levels of perception between the continental scale and that of the landscape
cite web: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)Other name, Château Johan-Beetz
Explore Quebec, travel itineraries in Quebec Find day trips, weekend getaway ideas and week-long itineraries. Parc Canada
There are three official emblems in Quebec: the yellow birch, the snowy owl and the versicolor iris.
cite book: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help)
|
Canada
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Motto: A mari usque ad mare (Latin) "From Sea to Sea" |
|||
| Anthem: "O Canada"
|
|||
 |
|||
| Capital | Ottawa 45°24′N 75°40′W / 45.400°N 75.667°W |
||
| Largest city | Toronto | ||
| Official languages | |||
| Demonym(s) | Canadian | ||
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy | ||
|
• Monarch
|
Charles III | ||
| Mary Simon | |||
| Mark Carney | |||
| Legislature | Parliament | ||
| Senate | |||
| House of Commons | |||
| Independence
from the United Kingdom
|
|||
| July 1, 1867 | |||
| December 11, 1931 | |||
| April 17, 1982 | |||
| Area | |||
|
• Total area
|
9,984,670 km2 (3,855,100 sq mi) (2nd) | ||
|
• Water (%)
|
11.76 (2015)[2] | ||
|
• Total land area
|
9,093,507 km2 (3,511,023 sq mi) | ||
| Population | |||
|
• 2025 Q1 estimate
|
|||
|
• 2021 census
|
|||
|
• Density
|
4.2/km2 (10.9/sq mi) (236th) | ||
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate | ||
|
• Total
|
|||
|
• Per capita
|
|||
| GDP | (nominal) | 2024 estimate | |
|
• Total
|
|||
|
• Per capita
|
|||
| Gini | (2024) | low inequality |
|
| HDI | (2022) | very high (18th) | |
| Currency | Canadian dollar ($) (CAD) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−3.5 to −8 | ||
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC−2.5 to −7 | ||
| Calling code | +1 | ||
| ISO 3166 code | CA | ||
| Internet TLD | .ca | ||
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's second-largest country by total area, with the world's longest coastline. Its border with the United States is the world's longest international land border. The country is characterized by a wide range of both meteorologic and geological regions. With a population of just over 41 million people, it has widely varying population densities, with the majority residing in urban areas and large areas of the country being sparsely populated. Canada's capital is Ottawa and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver.
Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces and territories resulting in the displacement of Indigenous populations, and a process of increasing autonomy from the United Kingdom. This increased sovereignty was highlighted by the Statute of Westminster, 1931, and culminated in the Canada Act 1982, which severed the vestiges of legal dependence on the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
Canada is a parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy in the Westminster tradition. The country's head of government is the prime minister, who holds office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the elected House of Commons and is appointed by the governor general, representing the monarch of Canada, the ceremonial head of state. The country is a Commonwealth realm and is officially bilingual (English and French) in the federal jurisdiction. It is very highly ranked in international measurements of government transparency, quality of life, economic competitiveness, innovation, education and human rights. It is one of the world's most ethnically diverse and multicultural nations, the product of large-scale immigration. Canada's long and complex relationship with the United States has had a significant impact on its history, economy, and culture.
A developed country, Canada has a high nominal per capita income globally and its advanced economy ranks among the largest in the world by nominal GDP, relying chiefly upon its abundant natural resources and well-developed international trade networks. Recognized as a middle power, Canada's strong support for multilateralism and internationalism has been closely related to its foreign relations policies of peacekeeping and aid for developing countries. Canada promotes its domestically shared values through participation in multiple international organizations and forums.
While a variety of theories have been postulated for the etymological origins of Canada, the name is now accepted as coming from the St. Lawrence Iroquoian word kanata, meaning "village" or "settlement".[8] In 1535, Indigenous inhabitants of the present-day Quebec City region used the word to direct French explorer Jacques Cartier to the village of Stadacona.[9] Cartier later used the word Canada to refer not only to that particular village but to the entire area subject to Donnacona (the chief at Stadacona);[9] by 1545, European books and maps had begun referring to this small region along the Saint Lawrence River as Canada.[9]
From the 16th to the early 18th century, Canada referred to the part of New France that lay along the Saint Lawrence River.[10] Following the British conquest of New France, this area was known as the British Province of Quebec from 1763 to 1791.[11] In 1791, the area became two British colonies called Upper Canada and Lower Canada. These two colonies were collectively referred to as the Canadas until their union as the Province of Canada in 1841.[12]
Upon Confederation in 1867, Canada was adopted as the legal name for the new country at the London Conference and the word dominion was conferred as the country's title.[13] By the 1950s, the term Dominion of Canada was no longer used by the United Kingdom, which considered Canada a "realm of the Commonwealth".[14]
The Canada Act 1982, which brought the Constitution of Canada fully under Canadian control, referred only to Canada. Later that year, the name of the national holiday was changed from Dominion Day to Canada Day.[15]
The first inhabitants of North America are generally hypothesized to have migrated from Siberia by way of the Bering land bridge and arrived at least 14,000 years ago.[16] The Paleo-Indian archeological sites at Old Crow Flats and Bluefish Caves are two of the oldest sites of human habitation in Canada.[17] The characteristics of Indigenous societies included permanent settlements, agriculture, complex societal hierarchies, and trading networks.[18] Some of these cultures had collapsed by the time European explorers arrived in the late 15th and early 16th centuries and have only been discovered through archeological investigations.[19] Indigenous peoples in present-day Canada include the First Nations, Inuit, and Métis,[20] the last being of mixed descent who originated in the mid-17th century when First Nations people married European settlers and their offspring subsequently developed their own identity.[20]

The Indigenous population at the time of the first European settlements is estimated to have been between 200,000[22] and two million,[23] with a figure of 500,000 accepted by Canada's Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples.[24] As a consequence of European colonization, the Indigenous population declined by forty to eighty percent.[25] The decline is attributed to several causes, including the transfer of European diseases, to which they had no natural immunity,[26] conflicts over the fur trade, conflicts with the colonial authorities and settlers, and the loss of Indigenous lands to settlers and the subsequent collapse of several nations' self-sufficiency.[27]
Although not without conflict, European Canadians' early interactions with First Nations and Inuit populations were relatively peaceful.[28] First Nations and Métis peoples played a critical part in the development of European colonies in Canada, particularly for their role in assisting European coureurs des bois and voyageurs in their explorations of the continent during the North American fur trade.[29] These early European interactions with First Nations would change from friendship and peace treaties to the dispossession of Indigenous lands through treaties.[30] From the late 18th century, European Canadians forced Indigenous peoples to assimilate into a western Canadian society.[31] Settler colonialism reached a climax in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.[32] A period of redress began with the formation of a reconciliation commission by the Government of Canada in 2008.[33] This included acknowledgment of cultural genocide,[34] settlement agreements,[33] and betterment of racial discrimination issues, such as addressing the plight of missing and murdered Indigenous women.[35]

It is believed that the first documented European to explore the east coast of Canada was Norse explorer Leif Erikson.[37] In approximately 1000 AD, the Norse built a small short-lived encampment that was occupied sporadically for perhaps 20 years at L'Anse aux Meadows on the northern tip of Newfoundland.[38] No further European exploration occurred until 1497, when seafarer John Cabot explored and claimed Canada's Atlantic coast in the name of Henry VII of England.[39] In 1534, French explorer Jacques Cartier explored the Gulf of Saint Lawrence where, on July 24, he planted a 10-metre (33 ft) cross bearing the words, "long live the King of France", and took possession of the territory New France in the name of King Francis I.[40] The early 16th century saw European mariners with navigational techniques pioneered by the Basque and Portuguese establish seasonal whaling and fishing outposts along the Atlantic coast.[41] In general, early settlements during the Age of Discovery appear to have been short-lived due to a combination of the harsh climate, problems with navigating trade routes and competing outputs in Scandinavia.[42]
In 1583, Sir Humphrey Gilbert, by the royal prerogative of Queen Elizabeth I, founded St John's, Newfoundland, as the first North American English seasonal camp.[43] In 1600, the French established their first seasonal trading post at Tadoussac along the Saint Lawrence.[38] French explorer Samuel de Champlain arrived in 1603 and established the first permanent year-round European settlements at Port Royal (in 1605) and Quebec City (in 1608).[44] Among the colonists of New France, Canadiens extensively settled the Saint Lawrence River valley and Acadians settled the present-day Maritimes, while fur traders and Catholic missionaries explored the Great Lakes, Hudson Bay, and the Mississippi watershed to Louisiana.[45] The Beaver Wars broke out in the mid-17th century over control of the North American fur trade.[46]
The English established additional settlements in Newfoundland in 1610 along with settlements in the Thirteen Colonies to the south.[47] A series of four wars erupted in colonial North America between 1689 and 1763; the later wars of the period constituted the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War.[48] Mainland Nova Scotia came under British rule with the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht and Canada and most of New France came under British rule in 1763 after the Seven Years' War.[49]

The Royal Proclamation of 1763 established First Nation treaty rights, created the Province of Quebec out of New France, and annexed Cape Breton Island to Nova Scotia.[15] St John's Island (now Prince Edward Island) became a separate colony in 1769.[51] To avert conflict in Quebec, the British Parliament passed the Quebec Act 1774, expanding Quebec's territory to the Great Lakes and Ohio Valley.[52] More importantly, the Quebec Act afforded Quebec special autonomy and rights of self-administration at a time when the Thirteen Colonies were increasingly agitating against British rule.[53] It re-established the French language, Catholic faith, and French civil law there, staving off the growth of an independence movement in contrast to the Thirteen Colonies.[54] The Proclamation and the Quebec Act in turn angered many residents of the Thirteen Colonies, further fuelling anti-British sentiment in the years prior to the American Revolution.[15]
After the successful American War of Independence, the 1783 Treaty of Paris recognized the independence of the newly formed United States and set the terms of peace, ceding British North American territories south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River to the new country.[55] The American war of independence also caused a large out-migration of Loyalists, the settlers who had fought against American independence. Many moved to Canada, particularly Atlantic Canada, where their arrival changed the demographic distribution of the existing territories. New Brunswick was in turn split from Nova Scotia as part of a reorganization of Loyalist settlements in the Maritimes, which led to the incorporation of Saint John, New Brunswick, as Canada's first city.[56] To accommodate the influx of English-speaking Loyalists in Central Canada, the Constitutional Act of 1791 divided the province of Canada into French-speaking Lower Canada (later Quebec) and English-speaking Upper Canada (later Ontario), granting each its own elected legislative assembly.[57]

The Canadas were the main front in the War of 1812 between the United States and the United Kingdom. Peace came in 1815; no boundaries were changed.[59] Immigration resumed at a higher level, with over 960,000 arrivals from Britain between 1815 and 1850.[60] New arrivals included refugees escaping the Great Irish Famine as well as Gaelic-speaking Scots displaced by the Highland Clearances.[61] Infectious diseases killed between 25 and 33 percent of Europeans who immigrated to Canada before 1891.[22]
The desire for responsible government resulted in the abortive Rebellions of 1837.[62] The Durham Report subsequently recommended responsible government and the assimilation of French Canadians into English culture.[15] The Act of Union 1840 merged the Canadas into a united Province of Canada and responsible government was established for all provinces of British North America east of Lake Superior by 1855.[63] The signing of the Oregon Treaty by Britain and the United States in 1846 ended the Oregon boundary dispute, extending the border westward along the 49th parallel. This paved the way for British colonies on Vancouver Island (1849) and in British Columbia (1858).[64] The Anglo-Russian Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1825) established the border along the Pacific coast, but, even after the US Alaska Purchase of 1867, disputes continued about the exact demarcation of the Alaska–Yukon and Alaska–British Columbia border.[65]

Following three constitutional conferences, the British North America Act, 1867 officially proclaimed Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867, initially with four provinces: Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick.[67] Canada assumed control of Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory to form the Northwest Territories, where the Métis' grievances ignited the Red River Rebellion and the creation of the province of Manitoba in July 1870.[68] British Columbia and Vancouver Island (which had been united in 1866) joined the confederation in 1871 on the promise of a transcontinental railway extending to Victoria in the province within 10 years,[69] while Prince Edward Island joined in 1873.[70] In 1898, during the Klondike Gold Rush in the Northwest Territories, Parliament created the Yukon Territory. Alberta and Saskatchewan became provinces in 1905.[70] Between 1871 and 1896, almost one quarter of the Canadian population emigrated south to the US.[71]
To open the West and encourage European immigration, the Government of Canada sponsored the construction of three transcontinental railways (including the Canadian Pacific Railway), passed the Dominion Lands Act to regulate settlement and established the North-West Mounted Police to assert authority over the territory.[72] This period of westward expansion and nation building resulted in the displacement of many Indigenous peoples of the Canadian Prairies to "Indian reserves",[73] clearing the way for ethnic European block settlements.[74] This caused the collapse of the Plains Bison in western Canada and the introduction of European cattle farms and wheat fields dominating the land.[75] The Indigenous peoples saw widespread famine and disease due to the loss of the bison and their traditional hunting lands.[76] The federal government did provide emergency relief, on condition of the Indigenous peoples moving to the reserves.[77] During this time, Canada introduced the Indian Act extending its control over the First Nations to education, government and legal rights.[78]
Because Britain still maintained control of Canada's foreign affairs under the British North America Act, 1867, its declaration of war in 1914 automatically brought Canada into the First World War.[79] Volunteers sent to the Western Front later became part of the Canadian Corps, which played a substantial role in the Battle of Vimy Ridge and other major engagements of the war.[80] The Conscription Crisis of 1917 erupted when the Unionist Cabinet's proposal to augment the military's dwindling number of active members with conscription was met with vehement objections from French-speaking Quebecers.[81] In 1919, Canada joined the League of Nations independently of Britain,[80] and the Statute of Westminster, 1931, affirmed Canada's independence.[82]
The Great Depression in Canada during the early 1930s saw an economic downturn, leading to hardship across the country.[83] In response to the downturn, the Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF) in Saskatchewan introduced many elements of a welfare state (as pioneered by Tommy Douglas) in the 1940s and 1950s.[84] On the advice of Prime Minister William Lyon Mackenzie King, war with Germany was declared effective September 10, 1939, by King George VI, seven days after the United Kingdom. The delay underscored Canada's independence.[80]
The first Canadian Army units arrived in Britain in December 1939. In all, over a million Canadians served in the armed forces during the Second World War.[85] Canadian troops played important roles in many key battles of the war, including the failed 1942 Dieppe Raid, the Allied invasion of Italy, the Normandy landings, the Battle of Normandy, and the Battle of the Scheldt in 1944.[80] Canada provided asylum for the Dutch monarchy while that country was occupied and is credited by the Netherlands for major contributions to its liberation from Nazi Germany.[86] Despite another conscription crisis in Quebec in 1944, Canada finished the war with a large army and strong economy.[87]
The financial crisis of the Great Depression led the Dominion of Newfoundland to relinquish responsible government in 1934 and become a Crown colony ruled by a British governor.[88] After two referendums, Newfoundlanders voted to join Canada in 1949 as a province.[89]
Canada's post-war economic growth, combined with the policies of successive Liberal governments, led to the emergence of a new Canadian identity, marked by the adoption of the maple leaf flag in 1965,[90] the implementation of official bilingualism (English and French) in 1969,[91] and the institution of official multiculturalism in 1971.[92] Socially democratic programs were also instituted, such as Medicare, the Canada Pension Plan, and Canada Student Loans; though, provincial governments, particularly Quebec and Alberta, opposed many of these as incursions into their jurisdictions.[93]

Finally, another series of constitutional conferences resulted in the Canada Act 1982, the patriation of Canada's constitution from the United Kingdom, concurrent with the creation of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.[95] Canada had established complete sovereignty as an independent country under its own monarchy.[96] In 1999, Nunavut became Canada's third territory after a series of negotiations with the federal government.[97]
At the same time, Quebec underwent profound social and economic changes through the Quiet Revolution of the 1960s, giving birth to a secular nationalist movement.[98] The radical Front de libération du Québec (FLQ) ignited the October Crisis with a series of bombings and kidnappings in 1970,[99] and the sovereigntist Parti Québécois was elected in 1976, organizing an unsuccessful referendum on sovereignty-association in 1980. Attempts to accommodate Quebec nationalism constitutionally through the Meech Lake Accord failed in 1990.[100] This led to the formation of the Bloc Québécois in Quebec and the invigoration of the Reform Party of Canada in the West.[101] A second referendum followed in 1995, in which sovereignty was rejected by a slimmer margin of 50.6 to 49.4 percent.[102] In 1997, the Supreme Court ruled unilateral secession by a province would be unconstitutional, and the Clarity Act was passed by Parliament, outlining the terms of a negotiated departure from Confederation.[100]
In addition to the issues of Quebec sovereignty, a number of crises shook Canadian society in the late 1980s and early 1990s. These included the explosion of Air India Flight 182 in 1985, the largest mass murder in Canadian history;[103] the École Polytechnique massacre in 1989, a university shooting targeting female students;[104] and the Oka Crisis of 1990,[105] the first of a number of violent confrontations between provincial governments and Indigenous groups.[106] Canada joined the Gulf War in 1990 and was active in several peacekeeping missions in the 1990s, including operations in the Balkans during and after the Yugoslav Wars,[107] and in Somalia, resulting in an incident that has been described as "the darkest era in the history of the Canadian military".[108] Canada sent troops to Afghanistan in 2001, resulting in the largest amount of Canadian deaths for any single military mission since the Korean War in the early 1950s.[109]
In 2011, Canadian forces participated in the NATO-led intervention into the Libyan Civil War[110] and also became involved in battling the Islamic State insurgency in Iraq in the mid-2010s.[111] The country celebrated its sesquicentennial in 2017; three years later, the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada began on January 27, 2020, causing widespread social and economic disruption.[112] In 2021, an announcement of the discovery of possible gravesites of over 200 Indigenous children found near a former Canadian Indian residential school, which aimed to assimilate Indigenous children for most of the 20th century, refocused media and public attention on the cultural genocide carried out against Canada's Indigenous peoples.[113][114] A trade war involving the United States, Canada, and Mexico began on February 1, 2025, when U.S. president Donald Trump signed orders imposing tariffs on goods from the two countries entering the United States.[115]

By total area (including its waters), Canada is the second-largest country.[116] By land area alone, Canada ranks fourth, due to having the world's largest area of fresh water lakes.[117] Stretching from the Atlantic Ocean in the east, along the Arctic Ocean to the north, and to the Pacific Ocean in the west, the country encompasses 9,984,670 square kilometres (3,855,100 sq mi) of territory.[118] Canada also has vast maritime terrain, with the world's longest coastline of 243,042 kilometres (151,019 mi).[119] In addition to sharing the world's largest land border with the United States—spanning 8,891 kilometres (5,525 mi)[a]—Canada shares a land border with Greenland (and hence the Kingdom of Denmark) to the northeast, on Hans Island,[120] and a maritime boundary with France's overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon to the southeast.[121] Canada is also home to the world's northernmost settlement, Canadian Forces Station Alert, on the northern tip of Ellesmere Island—latitude 82.5°N—which lies 817 kilometres (508 mi) from the North Pole.[122] In latitude, Canada's most northerly point of land is Cape Columbia in Nunavut at 83°6′41″N, with its southern extreme at Middle Island in Lake Erie at 41°40′53″N. In longitude, Canada's land extends from Cape Spear, Newfoundland, at 52°37'W, to Mount St. Elias, Yukon Territory, at 141°W.[123]
Canada can be divided into seven physiographic regions: the Canadian Shield, the interior plains, the Great Lakes–St. Lawrence Lowlands, the Appalachian region, the Western Cordillera, Hudson Bay Lowlands, and the Arctic Archipelago.[124] Boreal forests prevail throughout the country, ice is prominent in northern Arctic regions and through the Rocky Mountains, and the relatively flat Canadian Prairies in the southwest facilitate productive agriculture.[118] The Great Lakes feed the St. Lawrence River (in the southeast) where the lowlands host much of Canada's economic output.[118] Canada has over 2,000,000 lakes—563 of which are larger than 100 square kilometres (39 sq mi)—containing much of the world's fresh water.[125] There are also fresh-water glaciers in the Canadian Rockies, the Coast Mountains, and the Arctic Cordillera.[126] Canada is geologically active, having many earthquakes and potentially active volcanoes.[127]

Average winter and summer high temperatures across Canada vary from region to region. Winters can be harsh in many parts of the country, particularly in the interior and Prairie provinces, which experience a continental climate, where daily average temperatures are near −15 °C (5 °F), but can drop below −40 °C (−40 °F) with severe wind chills.[128] In non-coastal regions, snow can cover the ground for almost six months of the year, while in parts of the north snow can persist year-round. Coastal British Columbia has a temperate climate, with a mild and rainy winter. On the east and west coasts, average high temperatures are generally in the low 20s °C (70s °F), while between the coasts, the average summer high temperature ranges from 25 to 30 °C (77 to 86 °F), with temperatures in some interior locations occasionally exceeding 40 °C (104 °F).[129]
Much of Northern Canada is covered by ice and permafrost. The future of the permafrost is uncertain because the Arctic has been warming at three times the global average as a result of climate change in Canada.[130] Canada's annual average temperature over land has risen by 1.7 °C (3.1 °F), with changes ranging from 1.1 to 2.3 °C (2.0 to 4.1 °F) in various regions, since 1948.[118] The rate of warming has been higher across the North and in the Prairies.[131] In the southern regions of Canada, air pollution from both Canada and the United States—caused by metal smelting, burning coal to power utilities, and vehicle emissions—has resulted in acid rain, which has severely impacted waterways, forest growth, and agricultural productivity.[132] Canada is one of the largest greenhouse gas emitters globally,[133] with emissions increased by 16.5 percent between 1990 and 2022.[134]

Canada is divided into 15 terrestrial and five marine ecozones.[136] These ecozones encompass over 80,000 classified species of Canadian wildlife, with an equal number yet to be formally recognized or discovered.[137] Although Canada has a low percentage of endemic species compared to other countries,[138] due to human activities, invasive species, and environmental issues in the country, there are currently more than 800 species at risk of being lost.[139] About 65 percent of Canada's resident species are considered "Secure".[140] Over half of Canada's landscape is intact and relatively free of human development.[141] The boreal forest of Canada is considered to be the largest intact forest on Earth, with approximately 3,000,000 square kilometres (1,200,000 sq mi) undisturbed by roads, cities or industry.[142] Since the end of the last glacial period, Canada has consisted of eight distinct forest regions.[143]
Approximately 12.1 percent of the nation's landmass and freshwater are conservation areas, including 11.4 percent designated as protected areas.[144] Approximately 13.8 percent of its territorial waters are conserved, including 8.9 percent designated as protected areas.[144] Canada's first National Park, Banff National Park established in 1885 spans 6,641 square kilometres (2,564 sq mi).[145] Canada's oldest provincial park, Algonquin Provincial Park, established in 1893, covers an area of 7,653.45 square kilometres (2,955.01 sq mi).[146] Lake Superior National Marine Conservation Area is the world's largest freshwater protected area, spanning roughly 10,000 square kilometres (3,900 sq mi).[147] Canada's largest national wildlife region is the Scott Islands Marine National Wildlife Area which spans 11,570.65 square kilometres (4,467.45 sq mi).[148]

Canada is described as a "full democracy",[149] with a tradition of liberalism,[150] and an egalitarian,[151] moderate political ideology.[152] An emphasis on social justice has been a distinguishing element of Canada's political culture.[153] Peace, order, and good government, alongside an Implied Bill of Rights, are founding principles of Canadian federalism.[154]
At the federal level, Canada has been dominated by two relatively centrist parties practising "brokerage politics":[b] the centre-left leaning Liberal Party of Canada[157] and the centre-right leaning Conservative Party of Canada (or its predecessors).[158] The historically predominant Liberals position themselves at the centre of the political scale.[158] Five parties had representatives elected to the Parliament in the 2021 election—the Liberals, who formed a minority government; the Conservatives, who became the Official Opposition; the New Democratic Party (occupying the left[159]); the Bloc Québécois; and the Green Party.[160] Far-right and far-left politics have never been a prominent force in Canadian society.[161]
Canada has a parliamentary system within the context of a constitutional monarchy—the monarchy of Canada being the foundation of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.[162] The reigning monarch is also monarch of 14 other sovereign Commonwealth countries[163] and Canada's 10 provinces. The monarch appoints a representative, the governor general, on the advice of the prime minister, to carry out most of their ceremonial royal duties.[164]
The monarchy is the source of sovereignty and authority in Canada.[165] However, while the governor general or monarch may exercise their power without ministerial advice in rare crisis situations,[166] the use of the executive powers (or royal prerogative) is otherwise directed by the Cabinet, a committee of ministers of the Crown responsible to the elected House of Commons and chosen and headed by the prime minister,[167] the head of government. To ensure the stability of government, the governor general will usually appoint as prime minister the individual who is the current leader of the political party that can obtain the confidence of a majority of members in the House.[168] The Prime Minister's Office (PMO) is one of the most powerful institutions in government, initiating most legislation for parliamentary approval and selecting for appointment by the Crown the governor general, lieutenant governors, senators, federal court judges, and heads of Crown corporations and government agencies.[166] The leader of the party with the second-most seats usually becomes the leader of the Official Opposition and is part of an adversarial parliamentary system intended to keep the government in check.[169]

The Parliament of Canada passes all federal statute laws. It comprises the monarch, the House of Commons, and the Senate. While Canada inherited the British concept of parliamentary supremacy, this was later, with the enactment of the Constitution Act, 1982, all but completely superseded by the American notion of the supremacy of the law.[171]
Each of the 338 members of Parliament in the House of Commons is elected by simple plurality in an electoral district or riding. The Constitution Act, 1982, requires that no more than five years pass between elections, although the Canada Elections Act limits this to four years with a "fixed" election date in October; general elections still must be called by the governor general and can be triggered by either the advice of the prime minister or a lost confidence vote in the House.[172] The 105 members of the Senate, whose seats are apportioned on a regional basis, serve until age 75.[173]
Canadian federalism divides government responsibilities between the federal government and the 10 provinces. Provincial legislatures are unicameral and operate in parliamentary fashion similar to the House of Commons.[174] Canada's three territories also have legislatures, but these are not sovereign, have fewer constitutional responsibilities than the provinces,[175] and differ structurally from their provincial counterparts.[176]
The Constitution of Canada is the supreme law of the country and consists of written text and unwritten conventions.[177] The Constitution Act, 1867 (known as the British North America Act, 1867 prior to 1982), affirmed governance based on parliamentary precedent and divided powers between the federal and provincial governments.[178] The Statute of Westminster, 1931, granted full autonomy, and the Constitution Act, 1982, ended all legislative ties to Britain, as well as adding a constitutional amending formula and the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.[179] The Charter guarantees basic rights and freedoms that usually cannot be overridden by any government; a notwithstanding clause allows Parliament and the provincial legislatures to override certain sections of the Charter for a period of five years.[180]

Canada's judiciary interprets laws and has the power to strike down acts of Parliament that violate the constitution. The Supreme Court of Canada is the highest court, final arbiter, and has been led since 2017 by Richard Wagner, the Chief Justice of Canada.[181] The governor general appoints the court's nine members on the advice of the prime minister and minister of justice.[182] The federal Cabinet also appoints justices to superior courts in the provincial and territorial jurisdictions.[183]
Common law prevails everywhere except Quebec, where civil law predominates.[184] Criminal law is solely a federal responsibility and is uniform throughout Canada.[185] Law enforcement, including criminal courts, is officially a provincial responsibility, conducted by provincial and municipal police forces.[186] In most rural and some urban areas, policing responsibilities are contracted to the federal Royal Canadian Mounted Police.[187]
Canadian Aboriginal law provides certain constitutionally recognized rights to land and traditional practices for Indigenous groups in Canada.[188] Various treaties and case laws were established to mediate relations between Europeans and many Indigenous peoples.[189] The role of Aboriginal law and the rights they support were reaffirmed by section 35 of the Constitution Act, 1982.[189] These rights may include provision of services, such as healthcare through the Indian Health Transfer Policy, and exemption from taxation.[190]

Canada is a federation composed of 10 federated states, called provinces, and three federal territories. These may be grouped into four main regions: Western Canada, Central Canada, Atlantic Canada, and Northern Canada (Eastern Canada refers to Central Canada and Atlantic Canada together).[192] Provinces and territories have responsibility for social programs such as healthcare, education, and social programs,[193] as well as administration of justice (but not criminal law). Although the provinces collect more revenue than the federal government, equalization payments are made by the federal government to ensure reasonably uniform standards of services and taxation are kept between the richer and poorer provinces.[194]
The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their sovereignty from the Crown[195] and power and authority from the Constitution Act, 1867, whereas territorial governments have powers delegated to them by the Parliament of Canada[196] and the commissioners represent the King in his federal Council,[197] rather than the monarch directly. The powers flowing from the Constitution Act, 1867, are divided between the federal government and the provincial governments to exercise exclusively[198] and any changes to that arrangement require a constitutional amendment, while changes to the roles and powers of the territories may be performed unilaterally by the Parliament of Canada.[199]

Canada is recognized as a middle power for its role in global affairs with a tendency to pursue multilateral and international solutions.[201] Canada is known for its commitment to international peace and security, as well as being a mediator in conflicts,[202] and for providing aid to developing countries.[203]
Canada and the United States have a long and complex relationship;[204] they are close allies, co-operating regularly on military campaigns and humanitarian efforts.[205] Canada also maintains historic and traditional ties to the United Kingdom and to France,[206] along with both countries' former colonies through its membership in the Commonwealth of Nations and the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie.[207] Canada is noted for having a positive relationship with the Netherlands, owing, in part, to its contribution to the Dutch liberation during the Second World War.[86] Canada has diplomatic and consular offices in over 270 locations in approximately 180 foreign countries.[200]
Canada promotes its domestically shared values through participating in multiple international organizations.[208] Canada was a founding member of the United Nations (UN) in 1945 and formed the North American Aerospace Defense Command together with the United States in 1958.[209] The country has membership in the World Trade Organization, the Five Eyes, the G7 and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).[210] The country was a founding member the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum (APEC) in 1989 and joined the Organization of American States (OAS) in 1990.[211] Canada ratified the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) in 1948, and seven principal UN human rights conventions and covenants since then.[212]

Alongside many domestic obligations, more than 3,000 Canadian Armed Forces (CAF) personnel are deployed in multiple foreign military operations.[214] The Canadian unified forces comprise the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army, and Royal Canadian Air Force. The nation employs a professional, volunteer force of approximately 68,000 active personnel and 27,000 reserve personnel—increasing to 71,500 and 30,000 respectively under "Strong, Secure, Engaged"[215]—with a sub-component of approximately 5,000 Canadian Rangers.[216][c] In 2022, Canada's military expenditure totalled approximately $26.9 billion, or around 1.2 percent of the country's gross domestic product (GDP) – placing it 14th for military expenditure by country.[218]
Canada's role in developing peacekeeping and its participation in major peacekeeping initiatives during the 20th century has played a major role in its positive global image.[219] Peacekeeping is deeply embedded in Canadian culture and a distinguishing feature that Canadians feel sets their foreign policy apart from the United States.[220] Canada has long been reluctant to participate in military operations that are not sanctioned by the United Nations,[221] such as the Vietnam War or the 2003 invasion of Iraq.[221] Since the 21st century, Canadian direct participation in UN peacekeeping efforts has greatly declined.[222] The large decrease was a result of Canada directing its participation to UN-sanctioned military operations through the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, rather than directly through the UN.[223] The change to participation via NATO has resulted in a shift towards more militarized and deadly missions rather than traditional peacekeeping duties.[224]

Canada has a highly developed mixed-market economy,[226] with the world's ninth-largest economy as of 2023[update], and a nominal GDP of approximately US$2.221 trillion.[227] It is one of the world's largest trading nations, with a highly globalized economy.[228] In 2021, Canadian trade in goods and services reached $2.016 trillion.[229] Canada's exports totalled over $637 billion, while its imported goods were worth over $631 billion, of which approximately $391 billion originated from the United States.[229] In 2018, Canada had a trade deficit in goods of $22 billion and a trade deficit in services of $25 billion.[229] The Toronto Stock Exchange is the ninth-largest stock exchange in the world by market capitalization, listing over 1,500 companies with a combined market capitalization of over US$2 trillion.[230]
The Bank of Canada is the central bank of the country.[231] The minister of finance and minister of innovation, science, and industry use data from Statistics Canada to enable financial planning and develop economic policy.[232] Canada has a strong cooperative banking sector, with the world's highest per-capita membership in credit unions.[233] It ranks low in the Corruption Perceptions Index (14th in 2023)[234] and "is widely regarded as among the least corrupt countries of the world".[235] It ranks high in the Global Competitiveness Report (19th in 2024).[236] Canada's economy ranks above most Western nations on the Heritage Foundation's Index of Economic Freedom[237] and experiences a relatively low level of income disparity.[238] The country's average household disposable income per capita is "well above" the OECD average.[239] Canada ranks among the lowest of the most developed countries for housing affordability[240] and foreign direct investment.[241]
Since the early 20th century, the growth of Canada's manufacturing, mining, and service sectors has transformed the nation from a largely rural economy to an urbanized, industrial one.[242] The Canadian economy is dominated by the service industry, which employs about three-quarters of the country's workforce.[243] Canada has an unusually important primary sector, of which the forestry and petroleum industries are the most prominent components.[244] Many towns in northern Canada, where agriculture is difficult, are sustained by nearby mines or sources of timber.[245]

Canada's economic integration with the United States has increased significantly since the Second World War.[247] The Canada – United States Free Trade Agreement (FTA) of 1988 eliminated tariffs between the two countries, while the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) expanded the free-trade zone to include Mexico in 1994 (later replaced by the Canada–United States–Mexico Agreement).[248] As of 2023, Canada is a signatory to 15 free trade agreements with 51 different countries.[246]
Canada is one of the few developed nations that are net exporters of energy.[249] Atlantic Canada possess vast offshore deposits of natural gas,[250] and Alberta hosts the fourth-largest oil reserves in the world.[251] The vast Athabasca oil sands and other oil reserves give Canada 13 percent of global oil reserves, constituting the world's third- or fourth-largest.[252] Canada is additionally one of the world's largest suppliers of agricultural products; the Canadian Prairies region is one of the most important global producers of wheat, canola, and other grains.[253] The country is a leading exporter of zinc, uranium, gold, nickel, platinoids, aluminum, steel, iron ore, coking coal, lead, copper, molybdenum, cobalt, and cadmium.[254] Canada has a sizeable manufacturing sector centred in southern Ontario and Quebec, with automobiles and aeronautics representing particularly important industries.[255] The fishing industry is also a key contributor to the economy.[256]
In 2020, Canada spent approximately $41.9 billion on domestic research and development, with supplementary estimates for 2022 at $43.2 billion.[257] As of 2023[update], the country has produced 15 Nobel laureates in physics, chemistry, and medicine.[258] The country ranks seventh in the worldwide share of articles published in scientific journals, according to the Nature Index,[259] and is home to the headquarters of a number of global technology firms.[260] Canada has one of the highest levels of Internet access in the world, with over 33 million users, equivalent to around 94 percent of its total population.[261]

Canada's achievements in science and technology include the creation of the modern alkaline battery,[263] the discovery of insulin,[264] the development of the polio vaccine,[265] and discoveries about the interior structure of the atomic nucleus.[266] Other major Canadian scientific contributions include the artificial cardiac pacemaker, mapping the visual cortex,[267] the development of the electron microscope,[268] plate tectonics, deep learning, multi-touch technology, and the identification of the first black hole, Cygnus X-1.[269] Canada has a long history of discovery in genetics, which include stem cells, site-directed mutagenesis, T-cell receptor, and the identification of the genes that cause Fanconi anemia, cystic fibrosis, and early-onset Alzheimer's disease, among numerous other diseases.[270]
The Canadian Space Agency runs an active space program focused on deep-space, planetary, and aviation research, along with rockets and satellites.[271] Canada launched its first satellite, Alouette 1, in 1962.[272] It contributes to the International Space Station and is known for its robotic tools, such as multiple Canadarms.[273] Canada has initiated many long-term projects, including the Radarsat satellite series and the Black Brant rocket series.[274]
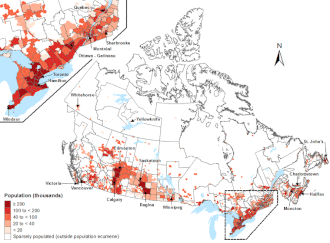
The 2021 Canadian census enumerated a total population of 36,991,981, an increase of around 5.2 percent over the 2016 figure.[276] It is estimated that Canada's population surpassed 40,000,000 in 2023.[277] The main drivers of population growth are immigration and, to a lesser extent, natural growth.[278] Canada has one of the highest per-capita immigration rates in the world,[279] driven mainly by economic policy and family reunification.[280] A record 405,000 immigrants were admitted in 2021.[281] Canada leads the world in refugee resettlement; it resettled more than 47,600 in 2022.[282] New immigrants settle mostly in major urban areas, such as Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver.[283]
Canada's population density, at 4.2 inhabitants per square kilometre (11/sq mi), is among the lowest in the world,[276] with approximately 95 percent of the population residing south of the 55th parallel north.[284] About 80 percent of the population lives within 150 kilometres (93 mi) of the border with the contiguous United States.[285] Canada is highly urbanized, with over 80 percent of the population living in urban centres.[286] The majority of Canadians (over 70 percent ) live below the 49th parallel, with 50 percent of Canadians living south of 45°42′ (45.7 degrees) north.[287] The most densely populated part of the country is the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor in Southern Quebec and Southern Ontario along the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River.[288]
The majority of Canadians (81.1 percent) live in family households, 12.1 percent report living alone, and 6.8 percent live with other relatives or unrelated persons.[289] Fifty-one percent of households are couples with or without children, 8.7 percent are single-parent households, 2.9 percent are multigenerational households, and 29.3 percent are single-person households.[289]
|
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Province | Pop. | Rank | Name | Province | Pop. | ||
| 1 | Toronto | Ontario | 6,202,225 | 11 | London | Ontario | 543,551 | ||
| 2 | Montreal | Quebec | 4,291,732 | 12 | Halifax | Nova Scotia | 465,703 | ||
| 3 | Vancouver | British Columbia | 2,642,825 | 13 | Niagara Region | Ontario | 433,604 | ||
| 4 | Ottawa–Gatineau | Ontario–Quebec | 1,488,307 | 14 | Windsor | Ontario | 422,630 | ||
| 5 | Calgary | Alberta | 1,481,806 | 15 | Oshawa | Ontario | 415,311 | ||
| 6 | Edmonton | Alberta | 1,418,118 | 16 | Victoria | British Columbia | 397,237 | ||
| 7 | Quebec City | Quebec | 839,311 | 17 | Saskatoon | Saskatchewan | 317,480 | ||
| 8 | Winnipeg | Manitoba | 834,678 | 18 | Regina | Saskatchewan | 249,217 | ||
| 9 | Hamilton | Ontario | 785,184 | 19 | Sherbrooke | Quebec | 227,398 | ||
| 10 | Waterloo Region | Ontario | 575,847 | 20 | Kelowna | British Columbia | 222,162 | ||
Respondents in the 2021 Canadian census self-reported over 450 "ethnic or cultural origins".[291] The major panethnic groups chosen were: European (52.5 percent), North American (22.9 percent), Asian (19.3 percent), North American Indigenous (6.1 percent), African (3.8 percent), Latin, Central and South American (2.5 percent), Caribbean (2.1 percent), Oceanian (0.3 percent), and other (6 percent).[292] Over 60 percent of Canadians reported a single origin, and 36 percent reported having multiple ethnic origins, thus the overall total is greater than 100 percent.[291]

The country's ten largest self-reported ethnic or cultural origins in 2021 were Canadian[d] (accounting for 15.6 percent of the population), followed by English (14.7 percent), Irish (12.1 percent), Scottish (12.1 percent), French (11.0 percent), German (8.1 percent), Chinese (4.7 percent), Italian (4.3 percent), Indian (3.7 percent), and Ukrainian (3.5 percent).[296]
Of the 36.3 million people enumerated in 2021, approximately 24.5 million reported being "White", representing 67.4 percent of the population.[297] The Indigenous population representing 5 percent or 1.8 million individuals, grew by 9.4 percent compared to the non-Indigenous population, which grew by 5.3 percent from 2016 to 2021.[297] One out of every four Canadians or 26.5 percent of the population belonged to a non-White and non-Indigenous visible minority,[298][e] the largest of which in 2021 were South Asian (2.6 million people; 7.1 percent), Chinese (1.7 million; 4.7 percent), Black (1.5 million; 4.3 percent), Filipinos (960,000 2.6 percent), Arabs (690,000; 1.9 percent), Latin Americans (580,000; 1.6 percent), Southeast Asians (390,000; 1.1 percent), West Asians (360,000; 1.0 percent), Koreans (220,000; 0.6 percent) and Japanese (99,000; 0.3 percent).[300]
Between 2011 and 2016, the visible minority population rose by 18.4 percent.[301] In 1961, about 300,000 people, less than two percent of Canada's population, were members of visible minority groups.[302] The 2021 census indicated that 8.3 million people, or almost one-quarter (23.0 percent) of the population, reported themselves as being or having been a landed immigrant or permanent resident in Canada—above the 1921 census previous record of 22.3 percent.[303] In 2021, India, China, and the Philippines were the top three countries of origin for immigrants moving to Canada.[304]

A multitude of languages are used by Canadians, with English and French (the official languages) being the mother tongues of approximately 54 percent and 19 percent of Canadians, respectively.[289] Canada's official bilingualism policies give citizens the right to receive federal government services in either English or French with official-language minorities guaranteed their own schools in all provinces and territories.[306]
Quebec's 1974 Official Language Act established French as the only official language of the province.[307] Although more than 82 percent of French-speaking Canadians live in Quebec, there are substantial Francophone populations in New Brunswick, Alberta, and Manitoba, with Ontario having the largest French-speaking population outside Quebec.[308] New Brunswick, the only officially bilingual province, has an Acadian French minority constituting 33 percent of the population.[309] There are also clusters of Acadians in southwestern Nova Scotia, on Cape Breton Island, and in central and western Prince Edward Island.[310]
Other provinces have no official languages as such, but French is used as a language of instruction, in courts, and for other government services, in addition to English. Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec allow for both English and French to be spoken in the provincial legislatures and laws are enacted in both languages. In Ontario, French has some legal status, but is not fully co-official.[311] There are 11 Indigenous language groups, composed of more than 65 distinct languages and dialects.[312] Several Indigenous languages have official status in the Northwest Territories.[313] Inuktitut is the majority language in Nunavut and is one of three official languages in the territory.[314]
As of the 2021 census, just over 7.8 million Canadians listed a non-official language as their first language. Some of the most common non-official first languages include Mandarin (679,255 first-language speakers), Punjabi (666,585), Cantonese (553,380), Spanish (538,870), Arabic (508,410), Tagalog (461,150), Italian (319,505), German (272,865), and Tamil (237,890).[289] The country is also home to many sign languages, some of which are Indigenous.[315] American Sign Language (ASL) is used across the country due to the prevalence of ASL in primary and secondary schools.[316] Quebec Sign Language (LSQ) is used primarily in Quebec.[317]

Canada is religiously diverse, encompassing a wide range of beliefs and customs.[319] The Constitution of Canada refers to God; however, Canada has no official church and the government is officially committed to religious pluralism.[320] Freedom of religion in Canada is a constitutionally protected right.[321]
Rates of religious adherence have steadily decreased since the 1970s.[319] With Christianity in decline after having once been central and integral to Canadian culture and daily life,[322] Canada has become a post-Christian, secular state.[323] Although the majority of Canadians consider religion to be unimportant in their daily lives,[324] they still believe in God.[325] The practice of religion is generally considered a private matter.[326]
According to the 2021 census, Christianity is the largest religion in Canada, with Roman Catholics representing 29.9 percent of the population having the most adherents. Christians overall representing 53.3 percent of the population,[f] are followed by people reporting irreligion or having no religion at 34.6 percent.[329] Other faiths include Islam (4.9 percent), Hinduism (2.3 percent), Sikhism (2.1 percent), Buddhism (1.0 percent), Judaism (0.9 percent), and Indigenous spirituality (0.2 percent).[330] Canada has the second-largest national Sikh population, behind India.[331]
Healthcare in Canada is delivered through the provincial and territorial systems of publicly funded health care, informally called Medicare.[332] It is guided by the provisions of the Canada Health Act of 1984[333] and is universal.[334] Universal access to publicly funded health services "is often considered by Canadians as a fundamental value that ensures national healthcare insurance for everyone wherever they live in the country".[335] Around 30 percent of Canadians' healthcare is paid for through the private sector.[336] This mostly pays for services not covered or partially covered by Medicare, such as prescription drugs, dentistry and optometry.[336] Approximately 65 to 75 percent of Canadians have some form of supplementary health insurance; many receive it through their employers or access secondary social service programs.[337]

In common with many other developed countries, Canada is experiencing an increase in healthcare expenditures due to a demographic shift toward an older population, with more retirees and fewer people of working age. In 2021, the average age in Canada was 41.9 years.[289] Life expectancy is 81.1 years.[338] A 2016 report by the chief public health officer found that 88 percent of Canadians, one of the highest proportions of the population among G7 countries, indicated that they "had good or very good health".[339] Eighty percent of Canadian adults self-report having at least one major risk factor for chronic disease: smoking, physical inactivity, unhealthy eating or excessive alcohol use.[340] Canada has one of the highest rates of adult obesity among OECD countries, contributing to approximately 2.7 million cases of diabetes.[340] Four chronic diseases—cancer (leading cause of death), cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, and diabetes—account for 65 percent of deaths in Canada.[341] There are approximately 8 million individuals aged 15 and older with one or more disabilities in Canada.[342]
In 2021, the Canadian Institute for Health Information reported that healthcare spending reached $308 billion, or 12.7 percent of Canada's GDP for that year.[343] In 2022, Canada's per-capita spending on health expenditures ranked 12th among health-care systems in the OECD.[344] Canada has performed close to, or above the average on the majority of OECD health indicators since the early 2000s, ranking above the average on OECD indicators for wait-times and access to care, with average scores for quality of care and use of resources.[345] The Commonwealth Fund's 2021 report comparing the healthcare systems of the 11 most developed countries ranked Canada second-to-last.[346] Identified weaknesses were comparatively higher infant mortality rate, the prevalence of chronic conditions, long wait times, poor availability of after-hours care, and a lack of prescription drugs and dental coverage.[346] An increasing problem in Canada's health system is a lack of healthcare professionals,[347] and hospital capacity.[348]

Education in Canada is for the most part provided publicly, funded and overseen by federal, provincial, and local governments.[350] Education is within provincial jurisdiction and a province's curriculum is overseen by its government.[351] Education in Canada is generally divided into primary education, followed by secondary and post-secondary education. Education in both English and French is available in most places across Canada.[352] Canada has a large number of universities, almost all of which are publicly funded.[353] Established in 1663, Université Laval is the oldest post-secondary institution in Canada.[354] The nation's three top ranking universities are the University of Toronto, McGill, and the University of British Columbia.[355] The largest university is the University of Toronto, which has over 85,000 students.[356]
According to a 2022 report by the OECD, Canada is one of the most educated countries in the world;[357] the country ranks first worldwide in the percentage of adults having tertiary education, with over 56 percent of Canadian adults having attained at least an undergraduate college or university degree.[358] Canada spends an average of 5.3 percent of its GDP on education.[359] The country invests heavily in tertiary education (more than US$20,000 per student).[360] As of 2022[update], 89 percent of adults aged 25 to 64 have earned the equivalent of a high-school degree, compared to an OECD average of 75 percent.[361]
The mandatory education age ranges between 5–7 to 16–18 years,[362] contributing to an adult literacy rate of 99 percent.[363] Just over 60,000 children are homeschooled in the country as of 2016. Canada is a well-performing OECD country in reading literacy, mathematics, and science, with the average student scoring 523.7, compared with the OECD average of 493 in 2015.[364]

Historically, Canada has been influenced by British, French, and Indigenous cultures and traditions.[366] During the 20th century, Canadians with African, Caribbean, and Asian nationalities have added to the Canadian identity and its culture.[367]
Canada's culture draws influences from its broad range of constituent nationalities, and policies that promote a just society are constitutionally protected.[368] Since the 1960s, Canada has emphasized human rights and inclusiveness for all its people.[369] The official state policy of multiculturalism is often cited as one of Canada's significant accomplishments[370] and a key distinguishing element of Canadian identity.[371] In Quebec, cultural identity is strong and there is a French Canadian culture that is distinct from English Canadian culture.[372] As a whole, Canada is in theory a cultural mosaic of regional ethnic subcultures.[373]
Canada's approach to governance emphasizing multiculturalism, which is based on selective immigration, social integration, and suppression of far-right politics, has wide public support.[374] Government policies such as publicly funded health care, higher taxation to redistribute wealth, the outlawing of capital punishment, strong efforts to eliminate poverty, strict gun control, a social liberal attitude toward women's rights (like pregnancy termination) and LGBT rights, and legalized euthanasia and cannabis use are indicators of Canada's political and cultural values.[375] Canadians also identify with the country's foreign aid policies, peacekeeping roles, the national park system, and the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.[376]

Themes of nature, pioneers, trappers, and traders played an important part in the early development of Canadian symbolism.[378] Modern symbols emphasize the country's geography, cold climate, lifestyles, and the Canadianization of traditional European and Indigenous symbols.[379] The use of the maple leaf as a Canadian symbol dates to the early 18th century. The maple leaf is depicted on Canada's current and previous flags and on the Arms of Canada.[380] Canada's official tartan, known as the "maple leaf tartan", reflects the colours of the maple leaf through the seasons—green in the spring, gold in the early autumn, red at the first frost, and brown after falling.[381] The Arms of Canada are closely modelled after those of the United Kingdom, with French and distinctive Canadian elements replacing or added to those derived from the British version.[382]
Other prominent symbols include the national motto, "A mari usque ad mare" ("From Sea to Sea"),[383] the sports of ice hockey and lacrosse, the beaver, Canada goose, common loon, Canadian horse, the Royal Canadian Mounted Police, the Canadian Rockies,[380] and, more recently, the totem pole and Inuksuk.[384] Canadian beer, maple syrup, tuques, canoes, nanaimo bars, butter tarts, and poutine are defined as uniquely Canadian.[385] Canadian coins feature many of these symbols: the loon on the $1 coin, the Arms of Canada on the 50¢ piece, and the beaver on the nickel.[386] An image of the monarch appears on $20 bank notes and the obverse of coins.[386]
Canadian literature is often divided into French- and English-language literatures, which are rooted in the literary traditions of France and Britain, respectively.[387] The earliest Canadian narratives were of travel and exploration.[388] This progressed into three major themes of historical Canadian literature: nature, frontier life, and Canada's position within the world, all of which tie into the garrison mentality.[389] In recent decades, Canada's literature has been strongly influenced by immigrants from around the world.[390] By the 1990s, Canadian literature was viewed as some of the world's best.[391]
Numerous Canadian authors have accumulated international literary awards,[392] including novelist, poet, and literary critic Margaret Atwood, who received two Booker Prizes;[393] Nobel laureate Alice Munro, who has been called the best living writer of short stories in English;[394] and Booker Prize recipient Michael Ondaatje, who wrote the novel The English Patient, which was adapted as a film of the same name that won the Academy Award for Best Picture.[395] L. M. Montgomery produced a series of children's novels beginning in 1908 with Anne of Green Gables.[396]

Canada's media is highly autonomous, uncensored, diverse, and very regionalized.[397] The Broadcasting Act declares "the system should serve to safeguard, enrich, and strengthen the cultural, political, social, and economic fabric of Canada".[398] Canada has a well-developed media sector, but its cultural output—particularly in English films, television shows, and magazines—is often overshadowed by imports from the United States.[399] As a result, the preservation of a distinctly Canadian culture is supported by federal government programs, laws, and institutions such as the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC), the National Film Board of Canada (NFB), and the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC).[400]
Canadian mass media, both print and digital, and in both official languages, is largely dominated by a "handful of corporations".[401] The largest of these corporations is the country's national public broadcaster, the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation, which also plays a significant role in producing domestic cultural content, operating its own radio and TV networks in both English and French.[402] In addition to the CBC, some provincial governments offer their own public educational TV broadcast services as well, such as TVOntario and Télé-Québec.[403]
Non-news media content in Canada, including film and television, is influenced both by local creators as well as by imports from the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, and France.[404] In an effort to reduce the amount of foreign-made media, government interventions in television broadcasting can include both regulation of content and public financing.[405] Canadian tax laws limit foreign competition in magazine advertising.[406]

Art in Canada is marked by thousands of years of habitation by Indigenous peoples,[408] and, in later times, artists have combined British, French, Indigenous, and American artistic traditions, at times embracing European styles while working to promote nationalism.[409] The nature of Canadian art reflects these diverse origins, as artists have taken their traditions and adapted these influences to reflect the reality of their lives in Canada.[410]
Modern painting in Canada has been greatly influenced by several major movements that have emerged over the years. One of the most prominent movements is the Group of Seven, which was founded in 1920, aimed to capture the wilderness in their artwork.[411] Associated with the group was Emily Carr, known for her landscapes and portrayals of the Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast.[412] The mid-20th century saw the rise of abstract art in Canada, with artists like Jean-Paul Riopelle and Paul-Émile Borduas.[413] The 1960s and 1970s saw the emergence of conceptual art, with artists such as Michael Snow and Ian Carr-Harris.[414] This era also saw the emergence of Indigenous artists like Norval Morrisseau, who combined traditional Indigenous techniques with modern art styles.[415] In more recent years, contemporary art has seen a revival of figurative art, with artists such as Kent Monkman and Shuvinai Ashoona.[416]

Canadian music reflects a variety of regional scenes.[418] Canada has developed a vast music infrastructure that includes church halls, chamber halls, conservatories, academies, performing arts centres, record companies, radio stations, and television music video channels.[419] Government support programs, such as the Canada Music Fund, assist a wide range of musicians and entrepreneurs who create, produce and market original and diverse Canadian music.[420] As a result of its cultural importance, as well as government initiatives and regulations, the Canadian music industry is one of the largest in the world,[421] producing internationally renowned composers, musicians, and ensembles.[422] Music broadcasting in the country is regulated by the CRTC.[423] The Canadian Academy of Recording Arts and Sciences presents Canada's music industry awards, the Juno Awards.[424] The Canadian Music Hall of Fame honours Canadian musicians for their lifetime achievements.[425]
Patriotic music in Canada dates back over 200 years. The earliest work of patriotic music in Canada, "The Bold Canadian", was written in 1812.[426] "The Maple Leaf Forever", written in 1866, was a popular patriotic song throughout English Canada and, for many years, served as an unofficial national anthem.[427] "O Canada" also served as an unofficial national anthem for much of the 20th century and was adopted as the country's official anthem in 1980.[428]

Canada's official national sports are ice hockey and lacrosse.[430] Other major professional games include curling, basketball, baseball, soccer, and football.[431] Great achievements in Canadian sports are recognized by numerous "Halls of Fame" and museums, such as Canada's Sports Hall of Fame.[432]
Canada shares several major professional sports leagues with the United States.[433] Canadian teams in these leagues include seven franchises in the National Hockey League, three Major League Soccer teams, and one team in each of Major League Baseball and the National Basketball Association. Other popular professional competitions include the Canadian Football League, National Lacrosse League, the Canadian Premier League, and the curling tournaments hosted by Curling Canada.[434] Canadians identified hockey as their preferred sport for viewing, followed by soccer and then basketball.[435]
In terms of participation, swimming was the most commonly reported sport by over one-third (35 percent) of Canadians in 2023.[436] This was closely followed by cycling (33 percent) and running (27 percent).[436] The popularity of specific sports varies;[437] in general, the Canadian-born population was more likely to have participated in winter sports such as ice hockey (the most popular young adult team sport),[436] skating, skiing and snowboarding, compared with immigrants, who were more likely to have played soccer (the most popular youth team sport),[438] tennis or basketball.[436] Sports such as golf, volleyball, badminton, bowling, and martial arts are also widely enjoyed at the youth and amateur levels.[439]
Canada has enjoyed success both at the Winter Olympics and at the Summer Olympics[440]—particularly the Winter Games as a "winter sports nation"—and has hosted high-profile international sporting events such as the 1976 Summer Olympics,[441] the 1988 Winter Olympics,[442] the 2010 Winter Olympics,[443] the 2015 FIFA Women's World Cup,[444] the 2015 Pan American Games and 2015 Parapan American Games.[445] The country is scheduled to co-host the 2026 FIFA World Cup alongside Mexico and the United States.[446]
In total, 165 Canadians died during the war in Afghanistan (158 soldiers, 7 civilians). More than 2,000 members of the CAF were wounded or injured during the war.
The new estimate indicates that there are about 80,000 known species in Canada, excluding viruses and bacteria
Canada's experience with human rights. Canada's experience can be divided into three phases: 1) Judicially implied rights; 2) Legislatively protected rights; and 3) Constitutionally protected human rights. Before human rights legislation and the Charter, courts in Canada relied on the theory of an "implied bill of rights" to protect traditional civil liberties such as freedom of speech and association. The theoretical foundation for these rights was the importance of free political speech and discussion in a democracy.
Two historically dominant political parties have avoided ideological appeals in favour of a flexible centrist style of politics that is often labelled brokerage politics
Canada's party system has long been described as a "brokerage system" in which the leading parties (Liberal and Conservative) follow strategies that appeal across major social cleavages in an effort to defuse potential tensions.
...most Canadian governments, especially in the federal sphere, have taken a moderate, centrist approach to decision making, seeking to balance growth, stability, and governmental efficiency and economy...
Social conservatives and the extreme right have had limited success designing the direction and policies of Canada's right-wing political parties.
Overview
Culture
Demography and statistics
Economy
Foreign relations and military
Geography and environment
Government and law
History
Social welfare
Overviews
Government
Travel